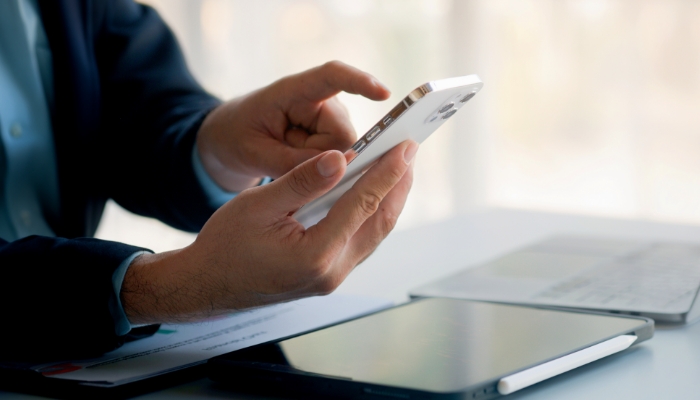
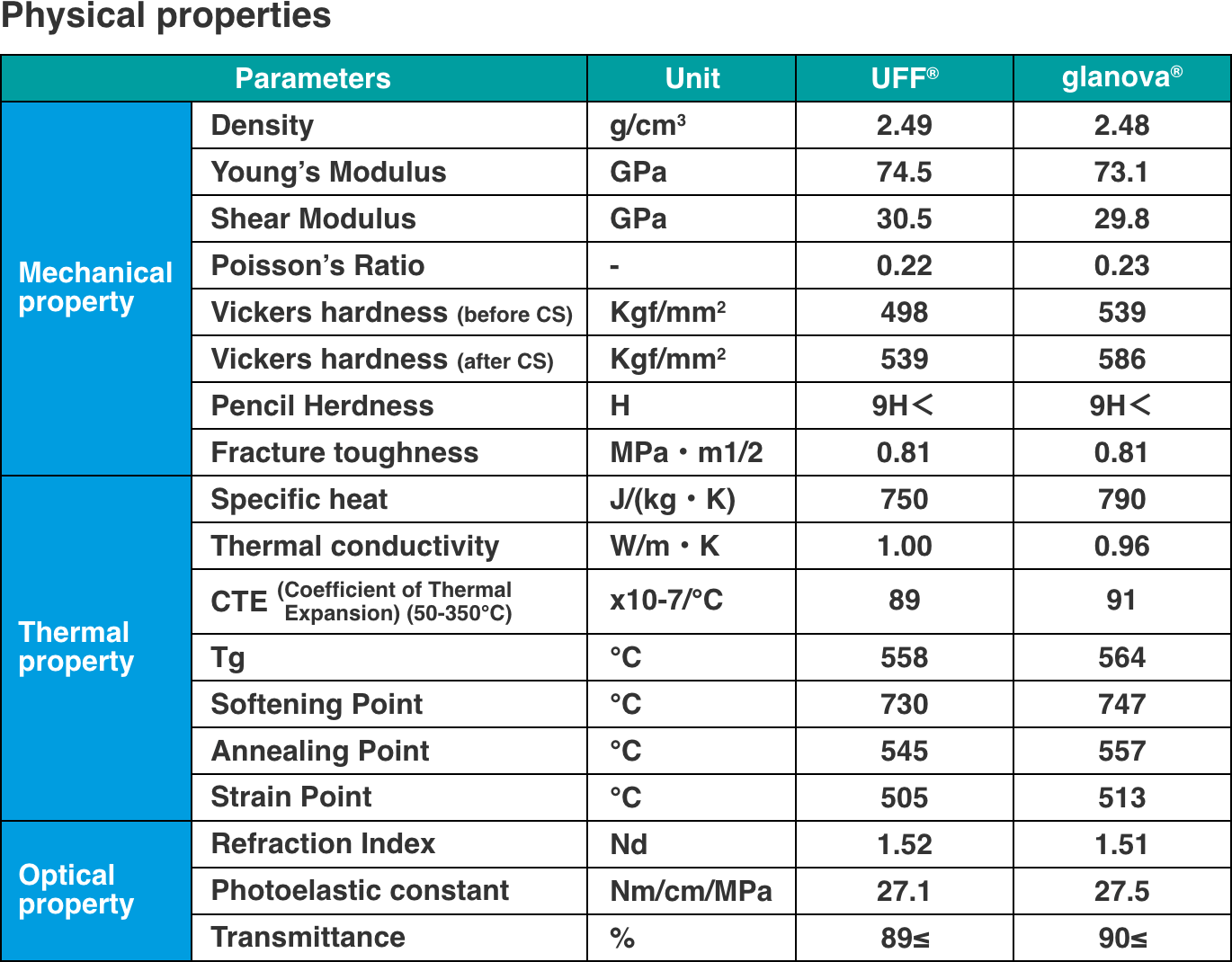
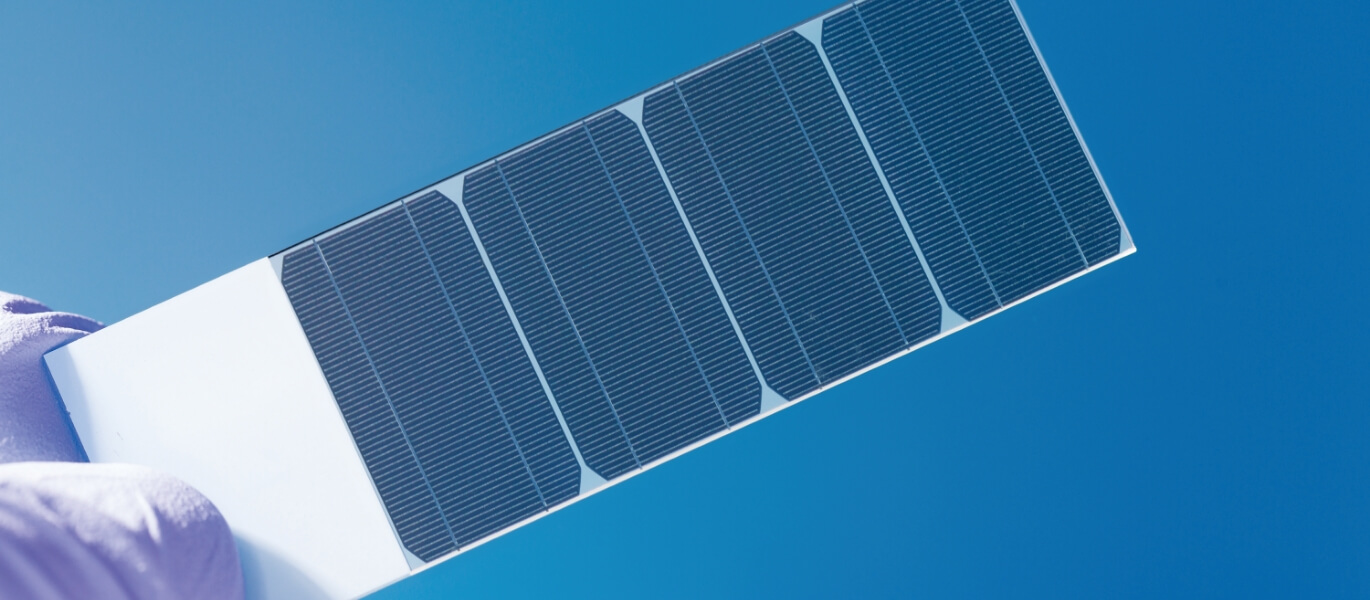
glanova® - Ultra-thin glass for chemical strengthening
High-strength, ultra-thin glass developed for chemical strengthening. It is ideal for cover glass of electronic devices such as various displays and smartphones, and its low softening point makes it easy to process and contributes to CO2 reduction.



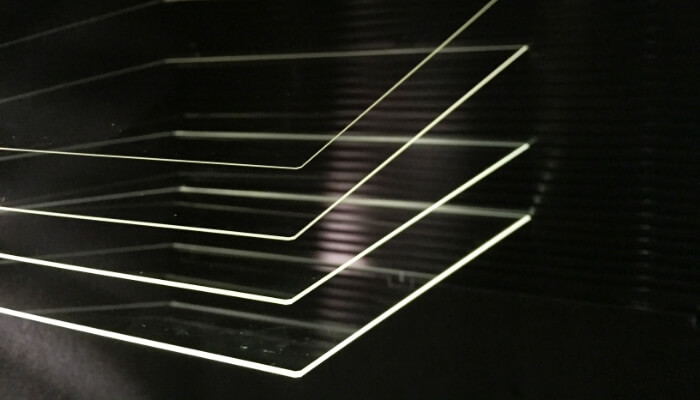
Product summary
glanova® is an ultra-thin sheet glass for chemical strengthening that is ideal for use as cover glass for automotive CIDs, clusters, and electronic devices. It is widely used in the automobile industry and the liquid crystal display industry in Japan and overseas. The Optical transmittance is over 90%, faithfully reproducing the colors of the display.
The low-cost aluminosilicate glass (glanova®), which has a uniquely developed glass composition, has excellent chemical strengthening properties. The softening point is about 700℃, which is almost the same as soda lime glass (UFF®). It has high impact resistance and realizes beautiful and luxurious cover glass.
Features of glanova®
glanova® is an ultra-thin glass with the following features and advantages.
■ Abundant plate thickness variations
0.33mm to 2.0mm
■ High quality and high flatness
■ low cost
Mass production and cost efficiency are achieved through the float method.
■ Special glass composition
Exhibits excellent chemical strengthening properties
■ HighOptical transmittance light transmittance
It has a low iron content and provides excellent color rendering in displays and screen printing.
■ Glass processing
- Cut
- Edge grinding
- Polishing
- Chemical strengthening
- Coating
- Bending
Application
glanova® is used for the following purposes.
- Touch panel display
- Smartphone
- Mobile tablet
- Computer cover display
- Glass for solar cell
- Cover glass for flat panel displays
- Vehicle touch screen (CID, cluster, etc.)
- Automotive Exterior Glass
- Special electronic applications

Environmentally friendly products
glanova® is made from pre-consumer recycled glass that more than 30% of materials such as trimmed glass from the manufacturing processes of float glass.
In addition, since the softening point of glass is low, the amount of heat required during thermoforming is small, making it an environmentally friendly product that reduces CO2 emissions.
glanova® was certified for recycling by SCS Global Services, a third-party company.

SCS Global Service
Low softening point and easy heat processing
The temperature required for thermoforming glanova® is about 700℃, which is almost the same as that of general soda glass.
It is ideal for applications that require curved surfaces because it can be thermoformed into curved shapes at low temperatures.
In addition, compared to other companies' aluminosilicate glass (glass for chemical strengthening)(Glass A in the table below), glanova® can keep the heating temperature required for thermoforming about 100-150℃ lower. Therefore, it can contribute to the reduction of power consumption and CO2 emissions by about 15-21%.
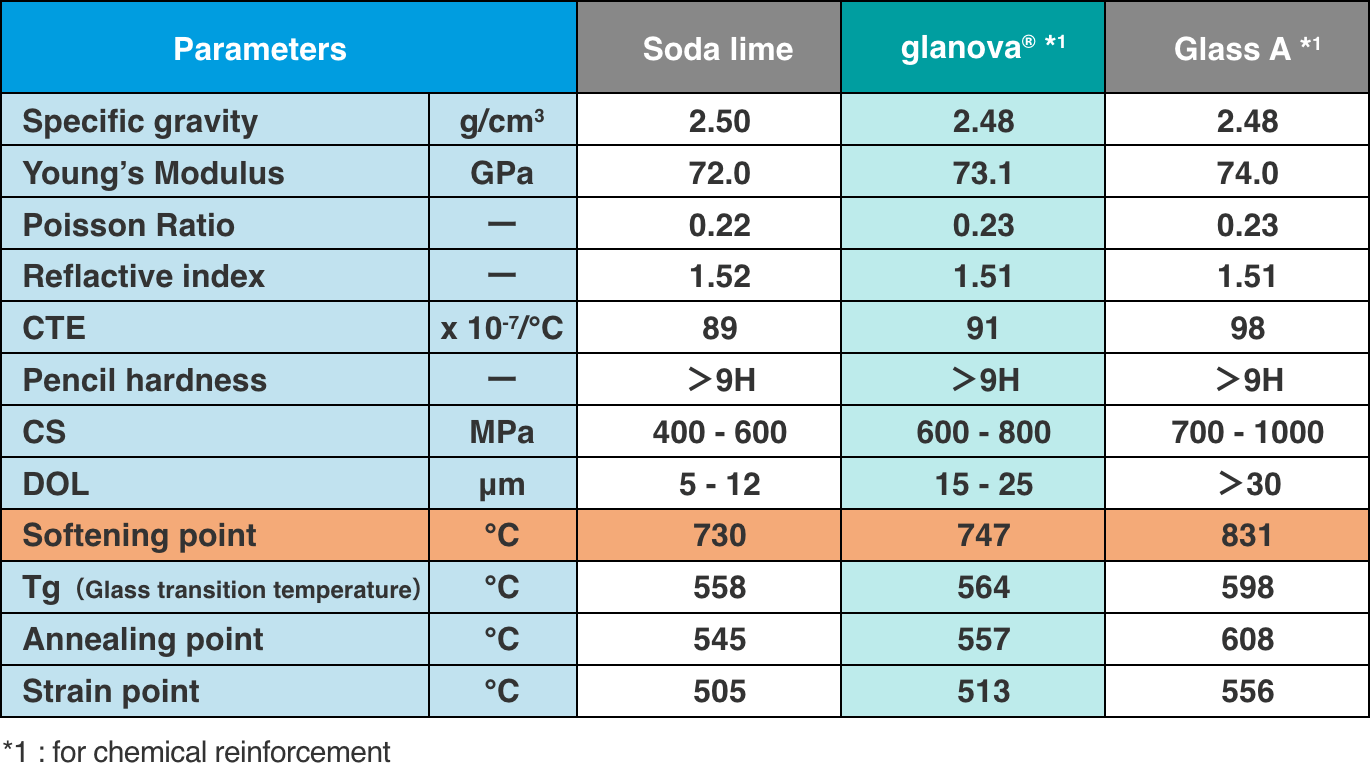
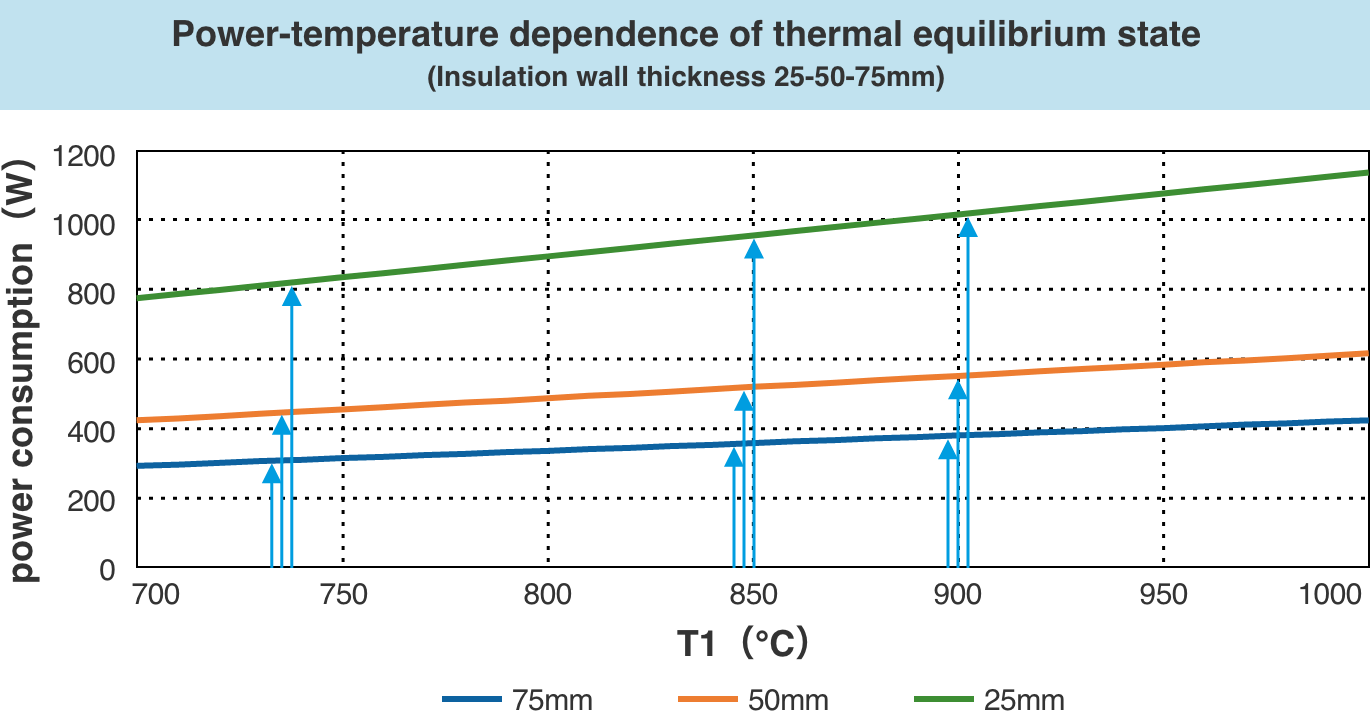
Even if the heat insulation performance of the hot bending furnace is improved, the ratio of power consumption due to the difference in heating temperature will not change.
The lower the heating temperature, the lower the power consumption, regardless of the insulation performance of the furnace.
Therefore, a difference in heating temperature of 100℃ causes a difference in power consumption of approximately 15%, and a difference of 150℃ causes a difference in power consumption of approximately 21%.
Chemical strengthening properties
Chemical strengthening is a strengthening method that generates compressive stress on the surface through ion exchange between sodium ions (Na+) contained in the glass composition and potassium ions (K+) in the molten salt. glanova® uses a glass composition that makes it easier to obtain the effect of chemical strengthening than soda-lime glass.
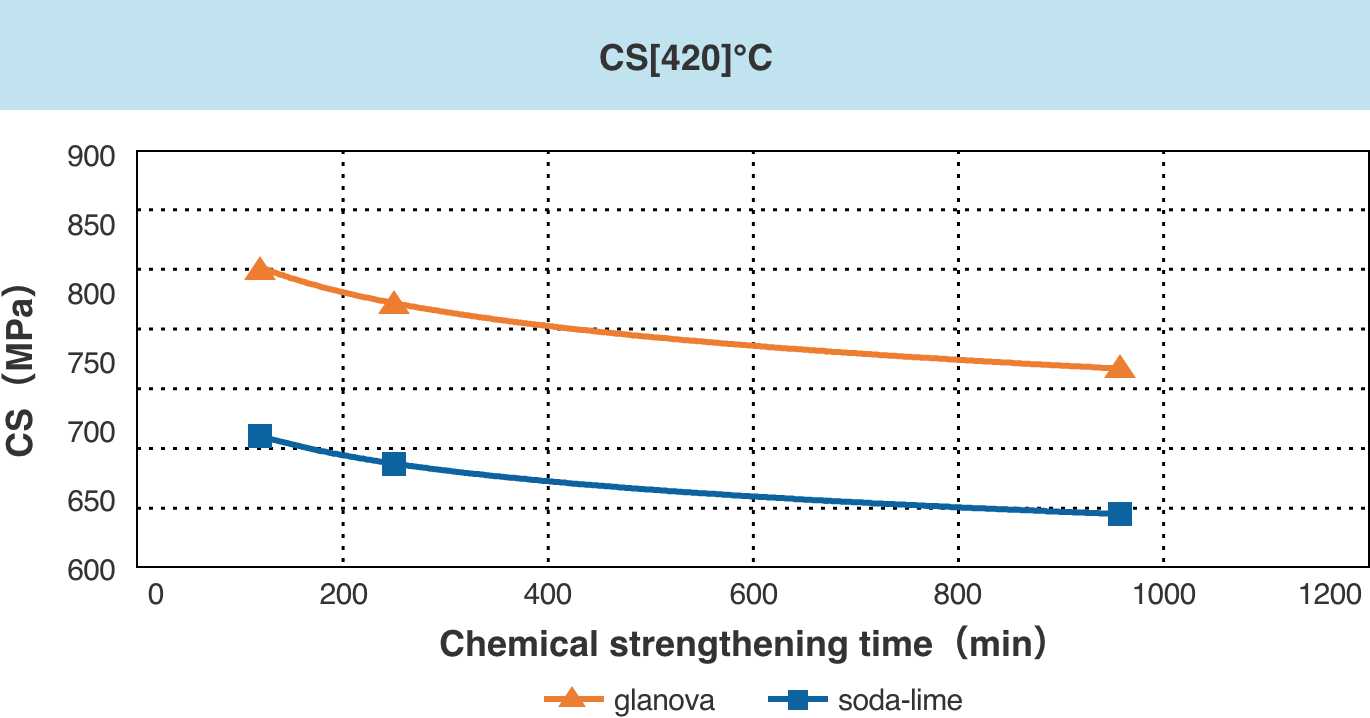
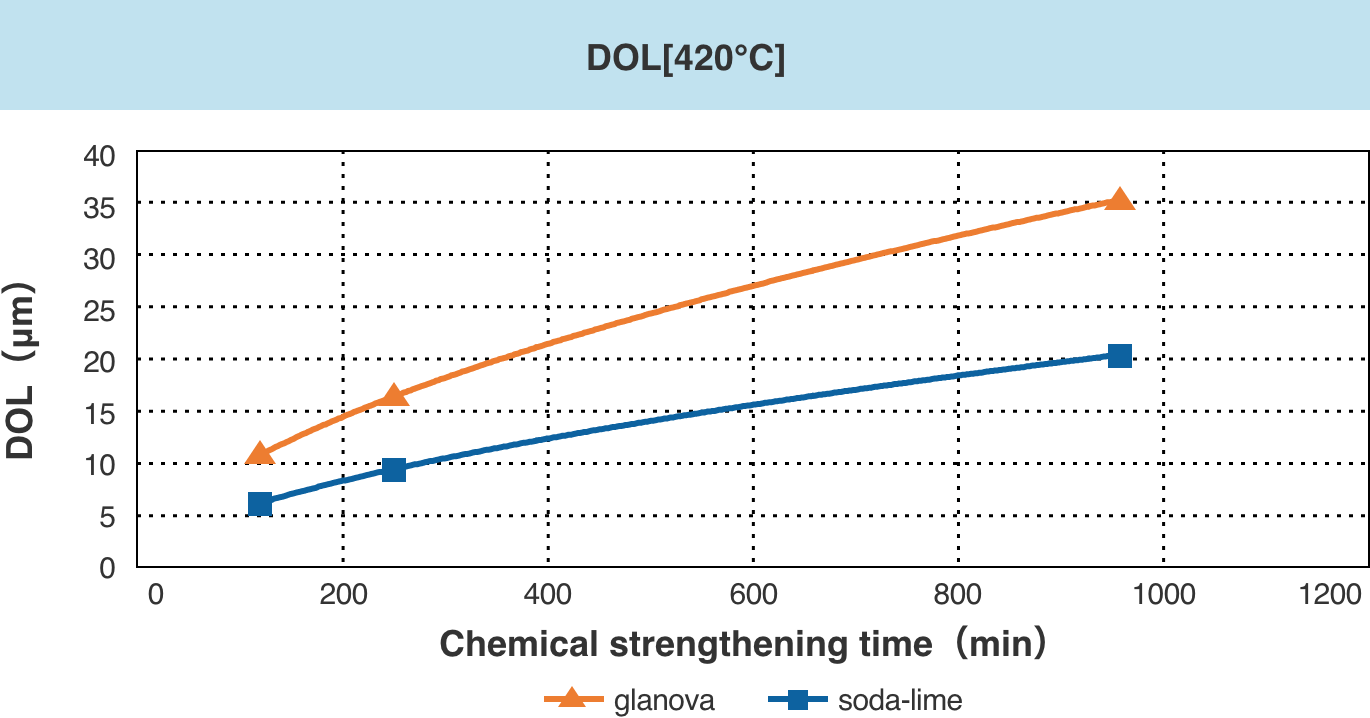
glanova® can be chemically strengthened to a higher degree (high CS/DOL) compared to general soda-lime glass.
* CS: Compressive stress (surface compressive stress)
* DOL : Depth of Layer
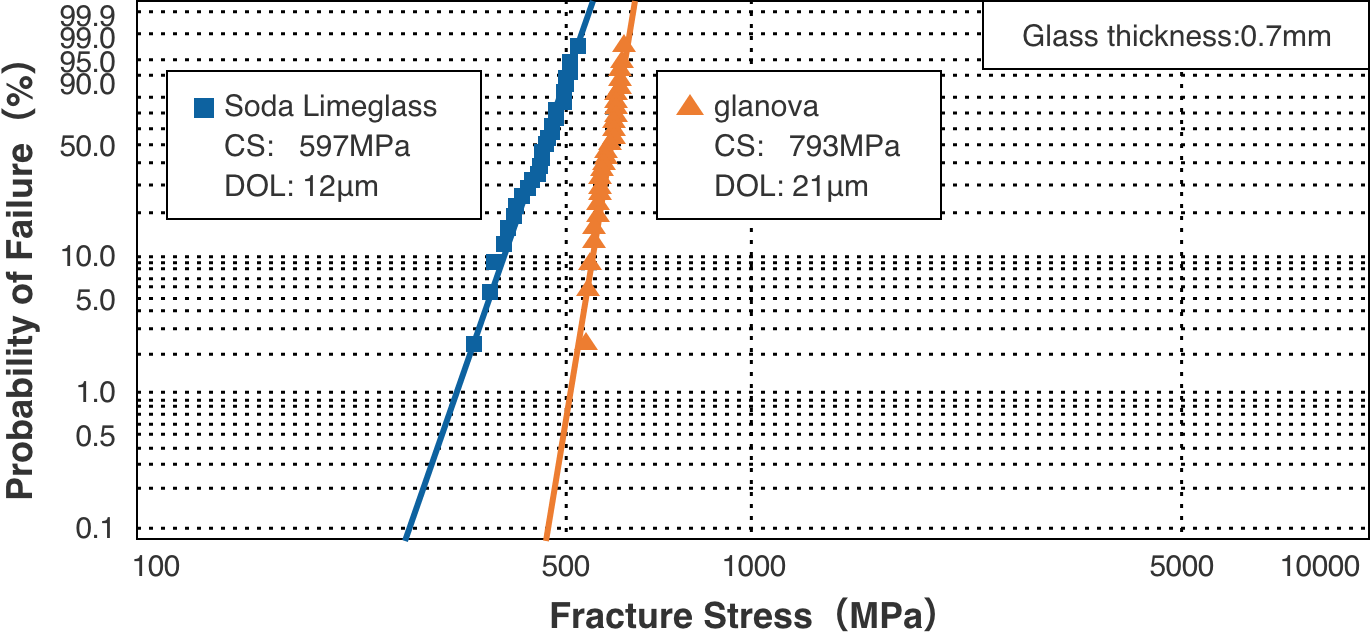
Compared to general soda-lime glass, glanova® exhibits high breaking strength even in a four-point bending test due to its more advanced chemical strengthening properties.
properties depending on aluminum content
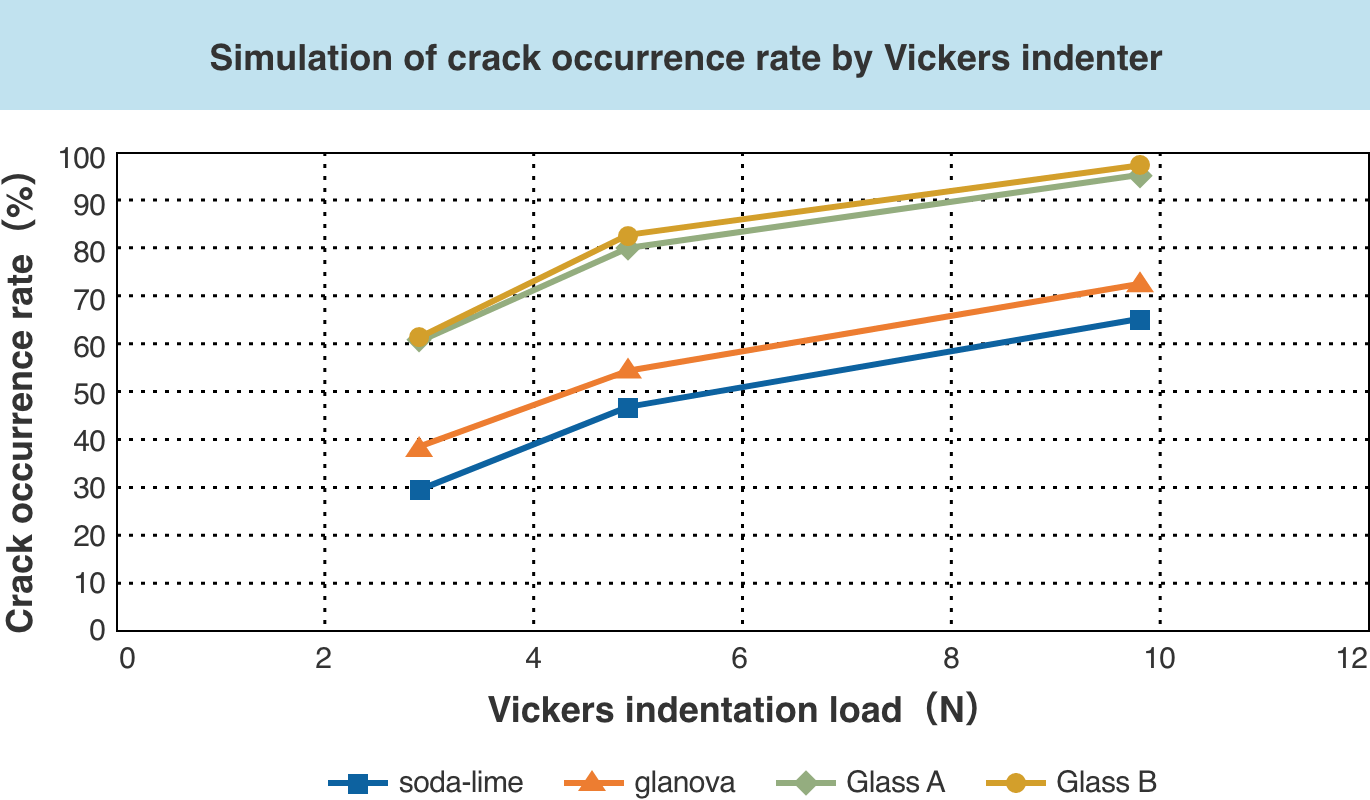
Crack occurrence rate of glass before chemical strengthening changes depending on aluminum content. (According to NSG research)
Aluminum content of glanova® is lower than chemically strengthened glass from other companies, but higher than soda-lime glass.
Compared to chemically strengthened glass from other companies (Glass A and B in the graph below), the crack occurrence rate of glanova® is about 20% lower.
In addition, when the glass breaks after chemical strengthening, fragments from glass breakage can maintain larger size, which helps preventing the glass from scattering.
glanova® is used in a variety of applications, because it also has superior chemical strengthening properties (high CS, DOL, etc.)
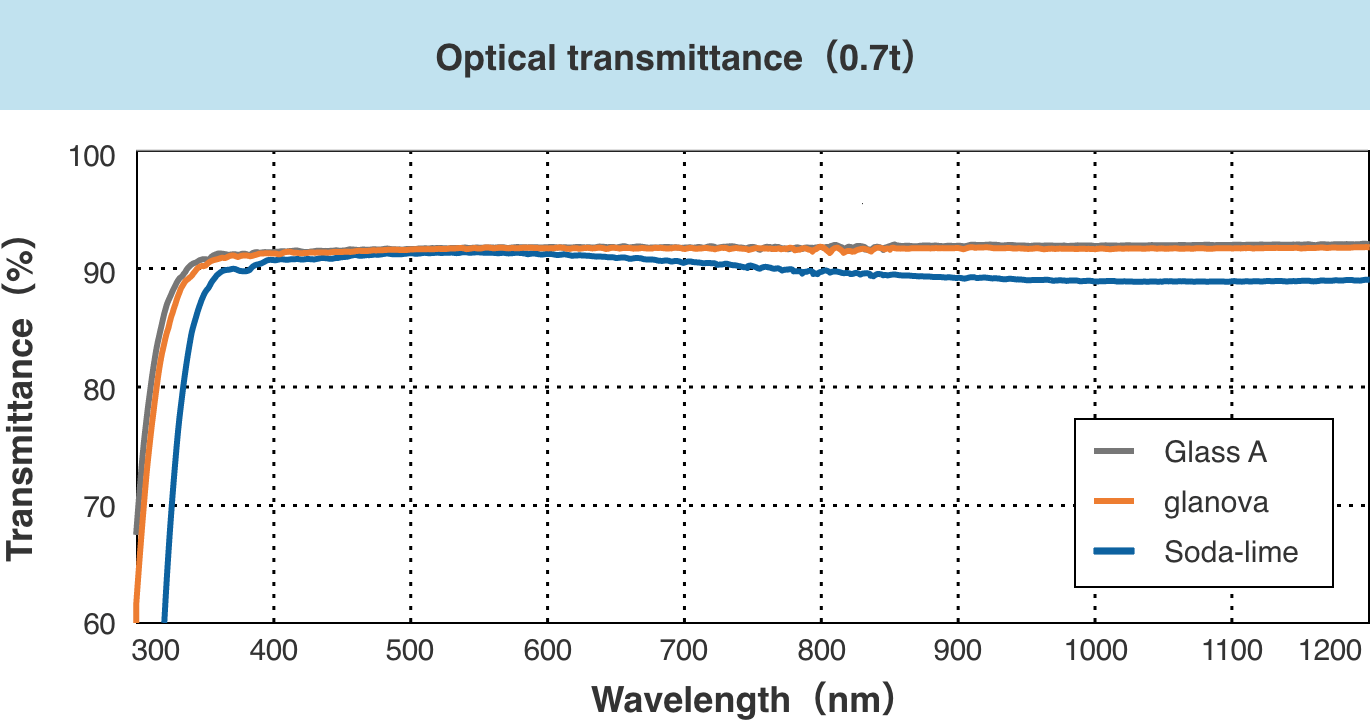
Optical properties
In the visible and near-infrared wavelength regions, glanova® has a higher transmittance than soda-lime glass and does not have a bluish tint, so printing colors can be reproduced faithfully.
Application example
Ultra-thin yet high-strength glanova® is mainly used as cover glass for various displays.
Especially in the automotive display field, where 3D shapes are required, it is highly evaluated by customers in Japan and overseas due to its easy thermoforming characteristics.
- Automotive Interior
- One Glass Solution(Capacitive Touch Panel)
For other uses, click here:Examples of Use

Anti-glare processing
This is a technology that scatters light by processing the surface of the glass into an uneven shape, giving it a function to reduce image reflection, and is mainly applied to the surface of glass for displays. Especially in the field of automotive displays and smartphones, it is being used for cover glass to create a sense of luxury. In addition, as the amount of information displayed on liquid crystals increases and the liquid crystal area expands, the need for such displays is increasing.

Issues with conventional anti-glare processing
Conventional anti-glare glass scatters transmitted light as well as reflected light, which has led to problems such as degraded image quality due to cloudiness (high haze) and reflection due to reflection of external light on the glass surface (high gloss).
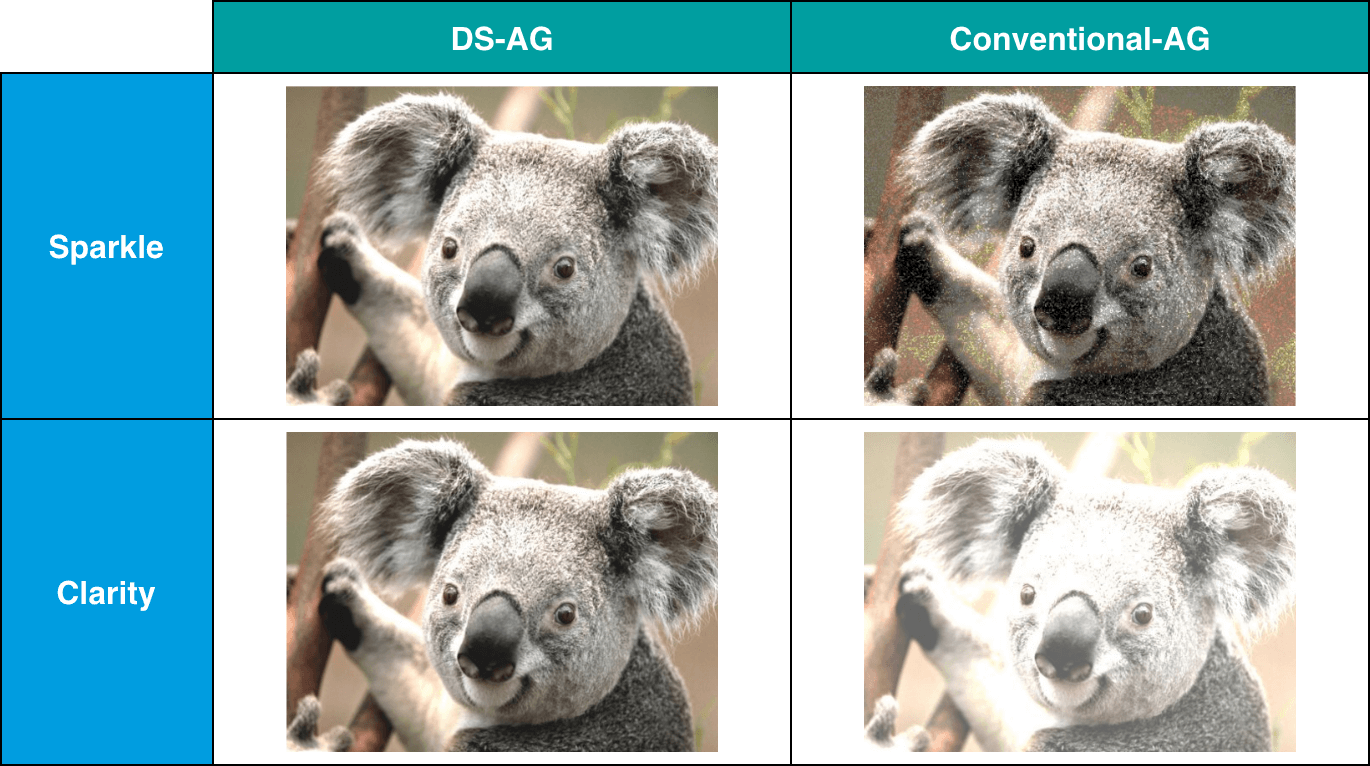
Proprietary anti-glare processing (DS-AG)
DS-AG, a processing technology developed by NSG, has made it possible to reduce reflected images (low gloss) and suppress white cloudiness (low haze).
By applying DS-AG processing to the glass surface of UFF® and glanova®, it is possible to suppress the reflection of external light on the surface and improve the visibility of the display.
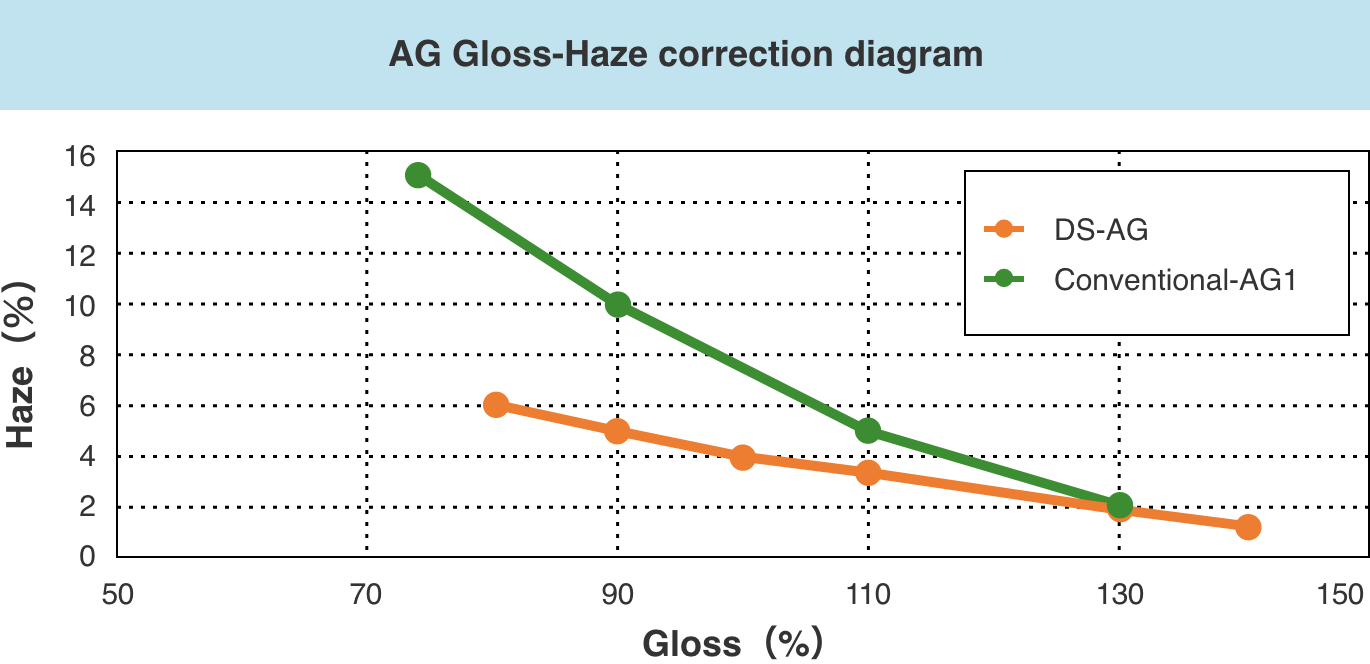
It is possible to achieve both suppression of reflections by low gloss and clear images by low haze.
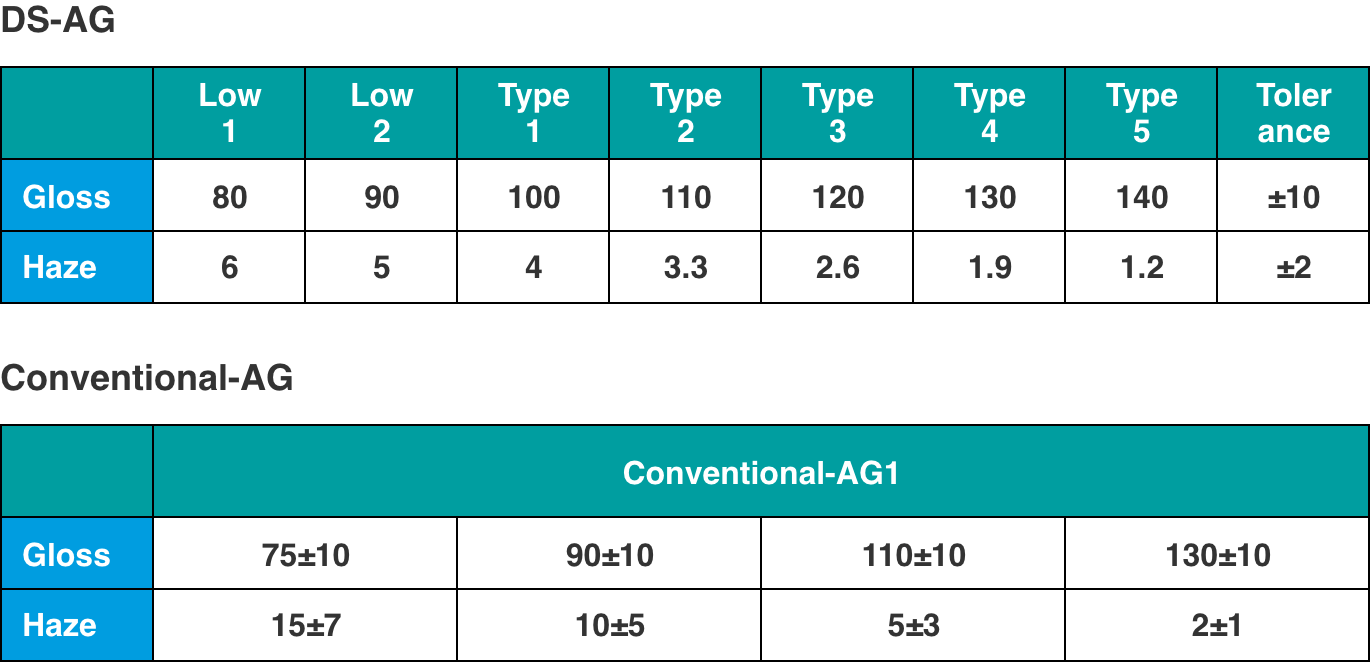
Control of dimples (irregularities on the glass surface) is possible
DS-AG uses photolithography technology to form dimples on the glass surface. Unlike the conventional anti-glare etching method, this makes it possible to control the shape and size of each dimple. By controlling the dimple size, DS-AG can suppress glare and white cloudiness.
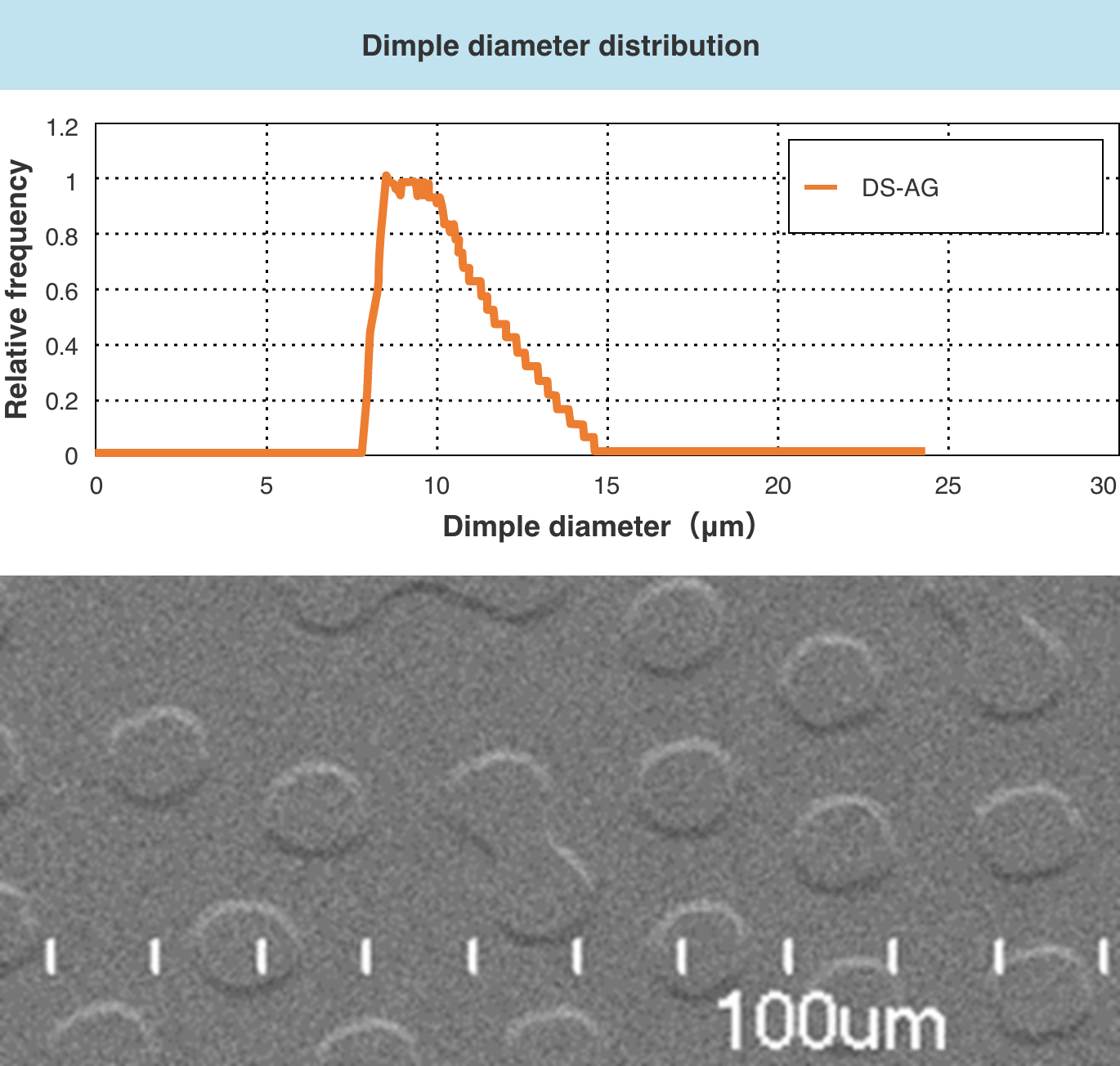
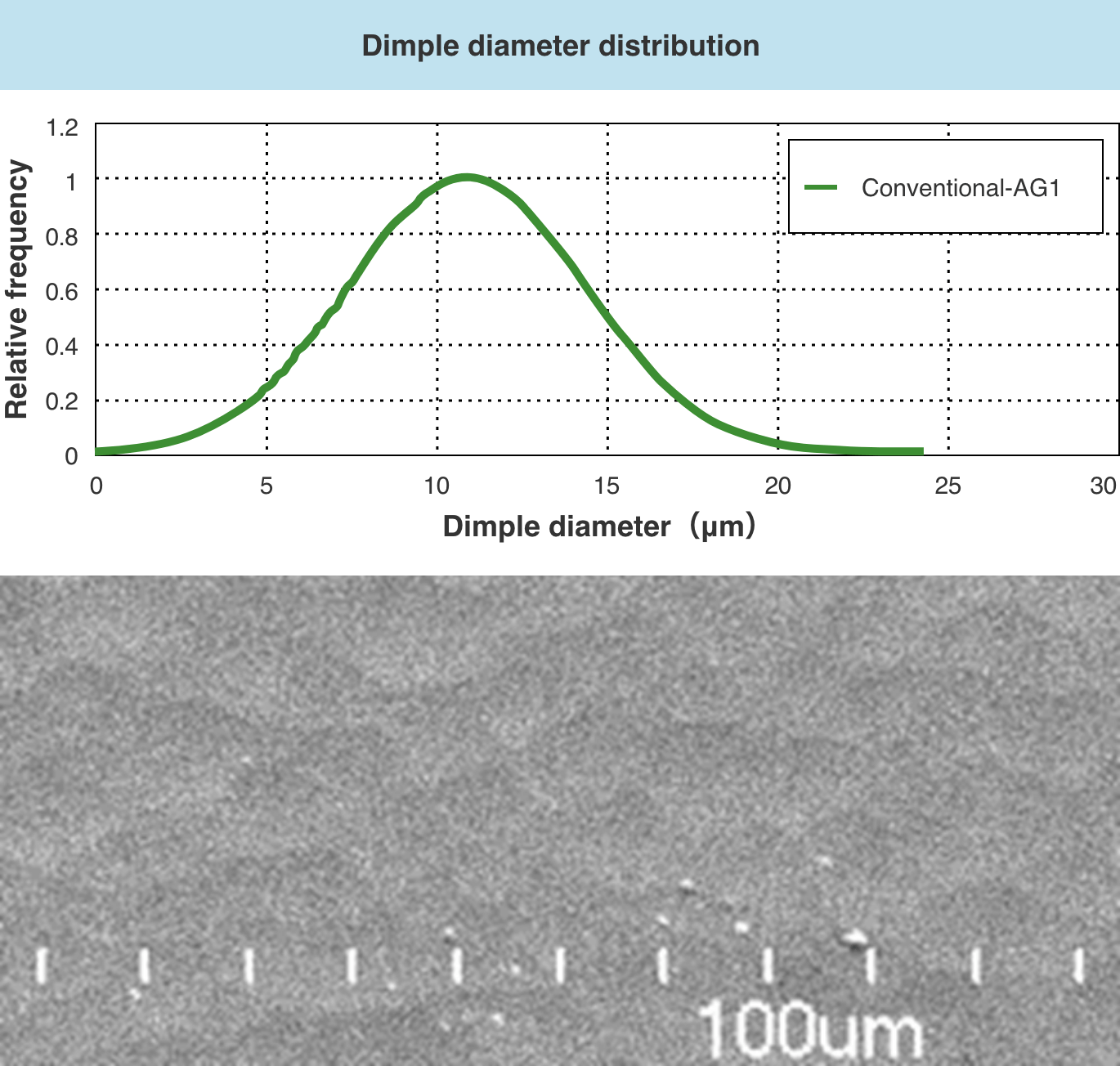
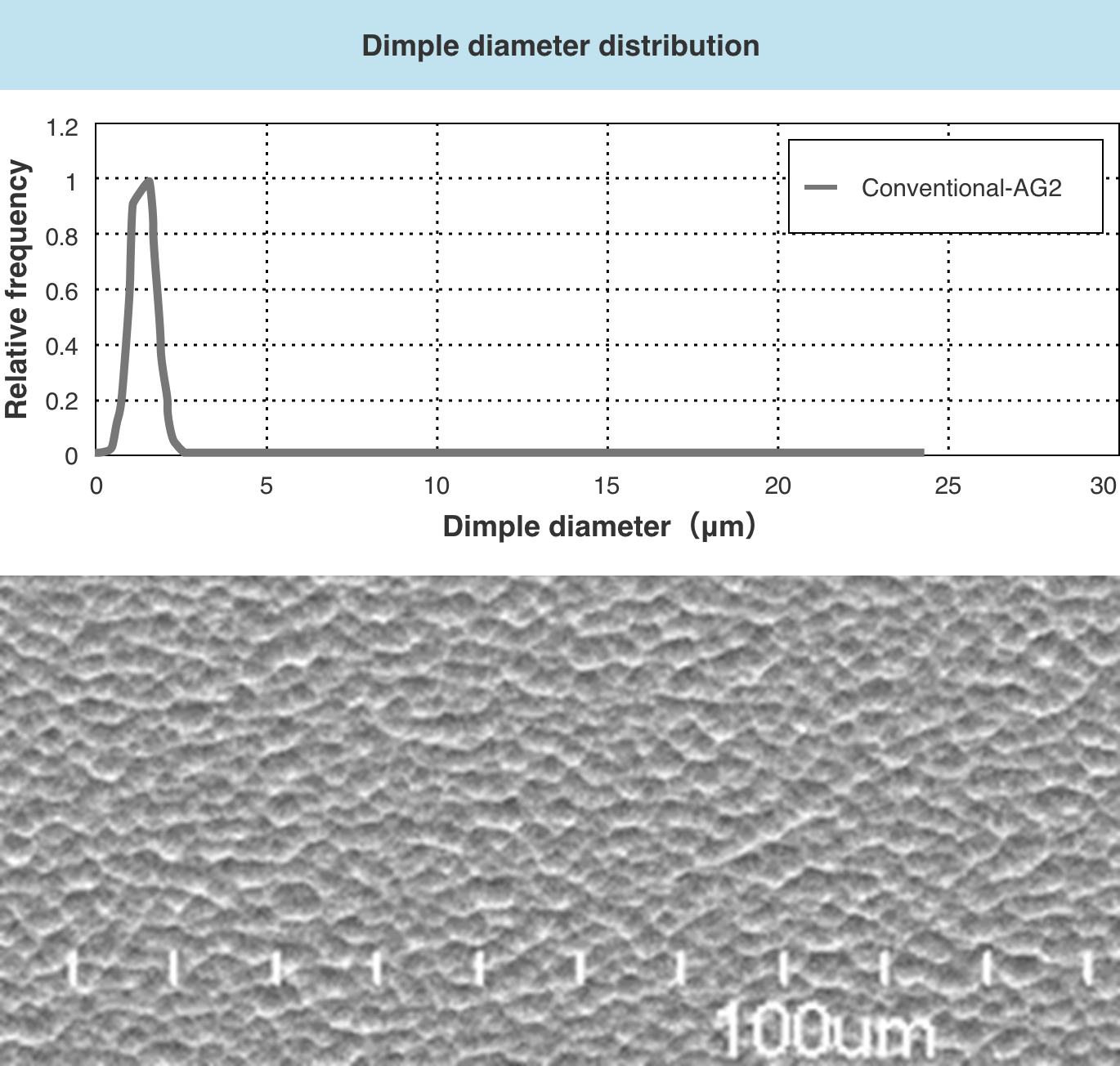
■ Reduce the maximum dimple
If the dimple size on the glass surface is close to the sub-pixel size or larger than 15 μm, the amount of light entering the field of view increases and sparkle occurs. However, DS-AG can suppress Sparkle by reducing the maximum dimple.
■ Increase the minimum dimple
If the dimple size on the glass surface is 3 μm or less, white cloudiness will occur and the clarity will decrease. however, DS-AG can suppress white cloudiness by increasing the minimum dimple.
Partial processing of DS-AG
DS-AG is anti-glare processed using photolithography technology, so it can be partially processed in μm units. This makes it possible to express the boundaries between the processed and unprocessed areas more clearly.

Anti-fingerprint DS-AG
By controlling the dimples, it contributes to the anti-fingerprint effect and longevity of the surface functions.
Evaluate the AF abrasion resistance of silbon paper with high wiping properties by changing the contact angle.
Reciprocating width: 50mm
Speed: 40Hz (40 round trips per minute)
Pressure area: 1㎠ (8 sheets of silbon paper stacked)
Paper replacement frequency: every 1K round trip
Load: 375g, 750g
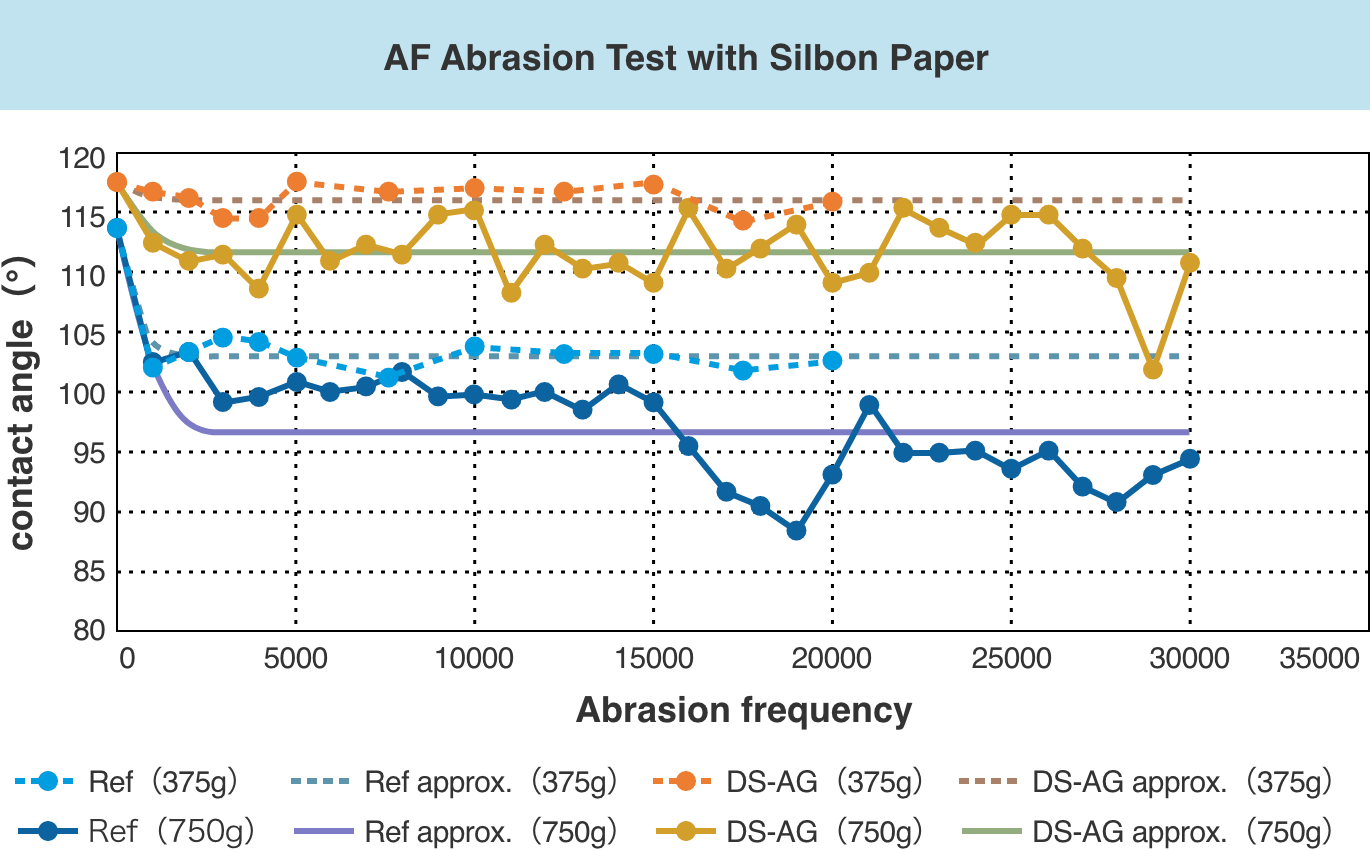
From this test result, it was found that the anti-fingerprint type DS-AG had less contact angle change than the existing AG (Ref.) under the same wear conditions.
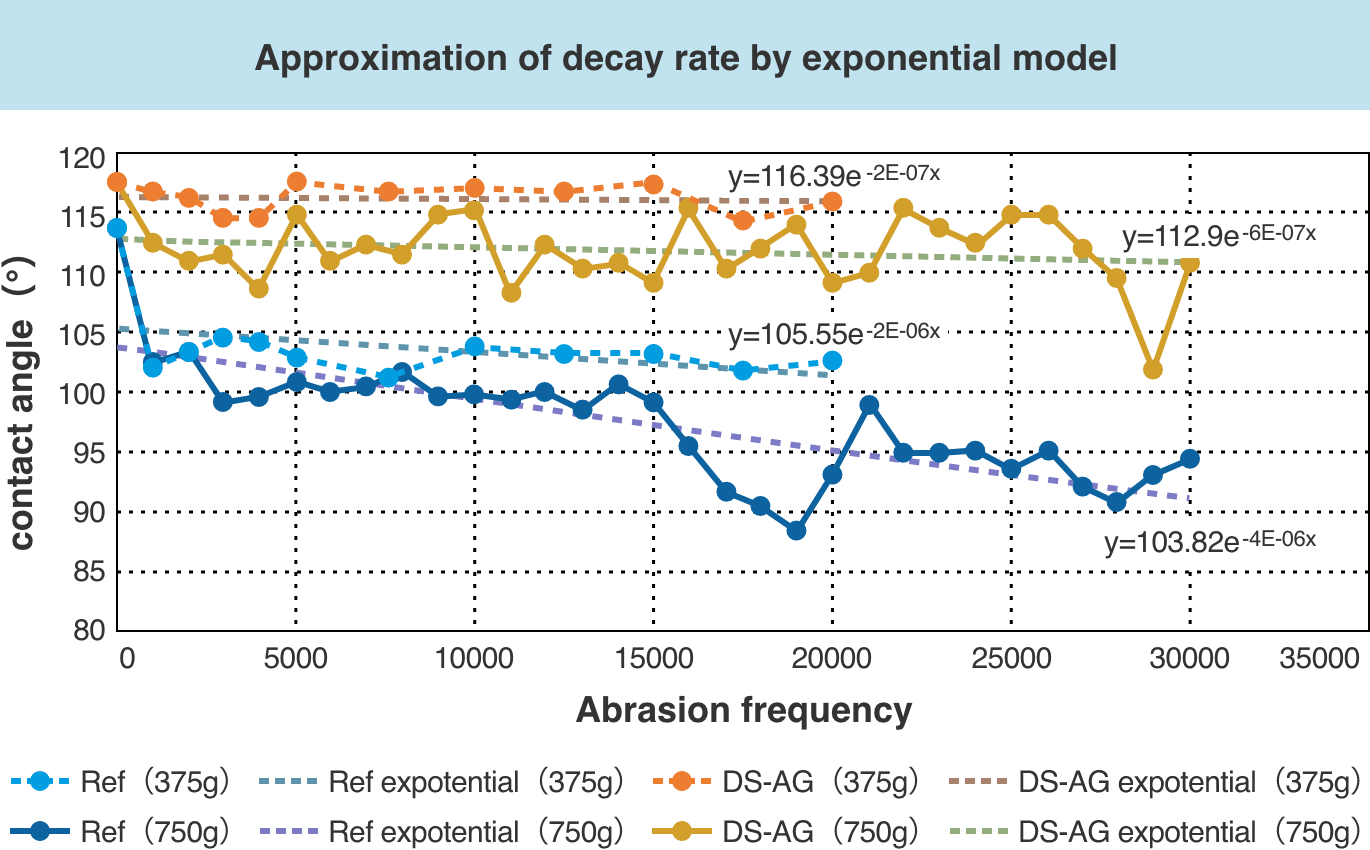
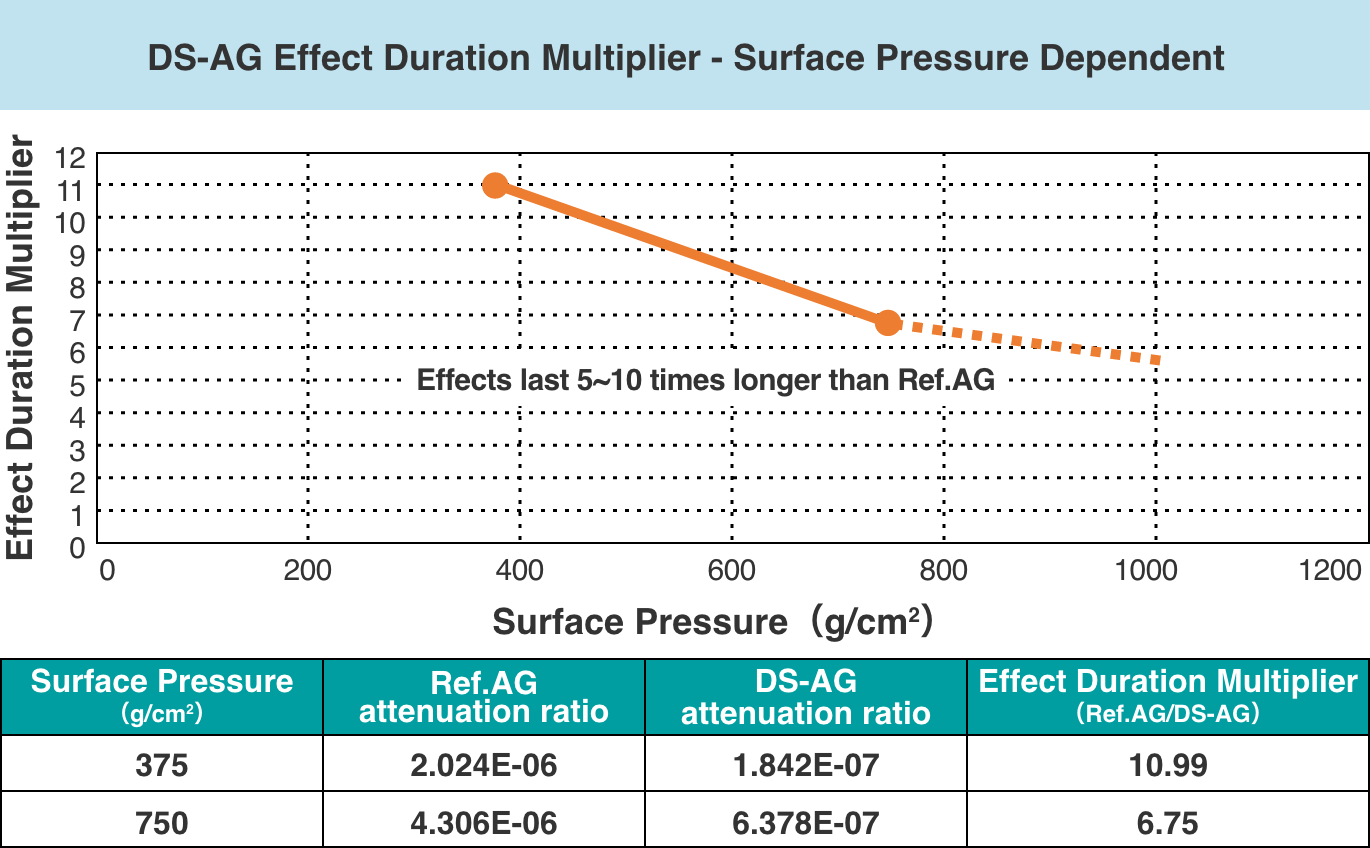
From this test result, it was found that the anti-fingerprint DS-AG was more than 5 times longer than the existing AG (Ref.) in the time to decrease to the same contact angle.
(Longer AF life)
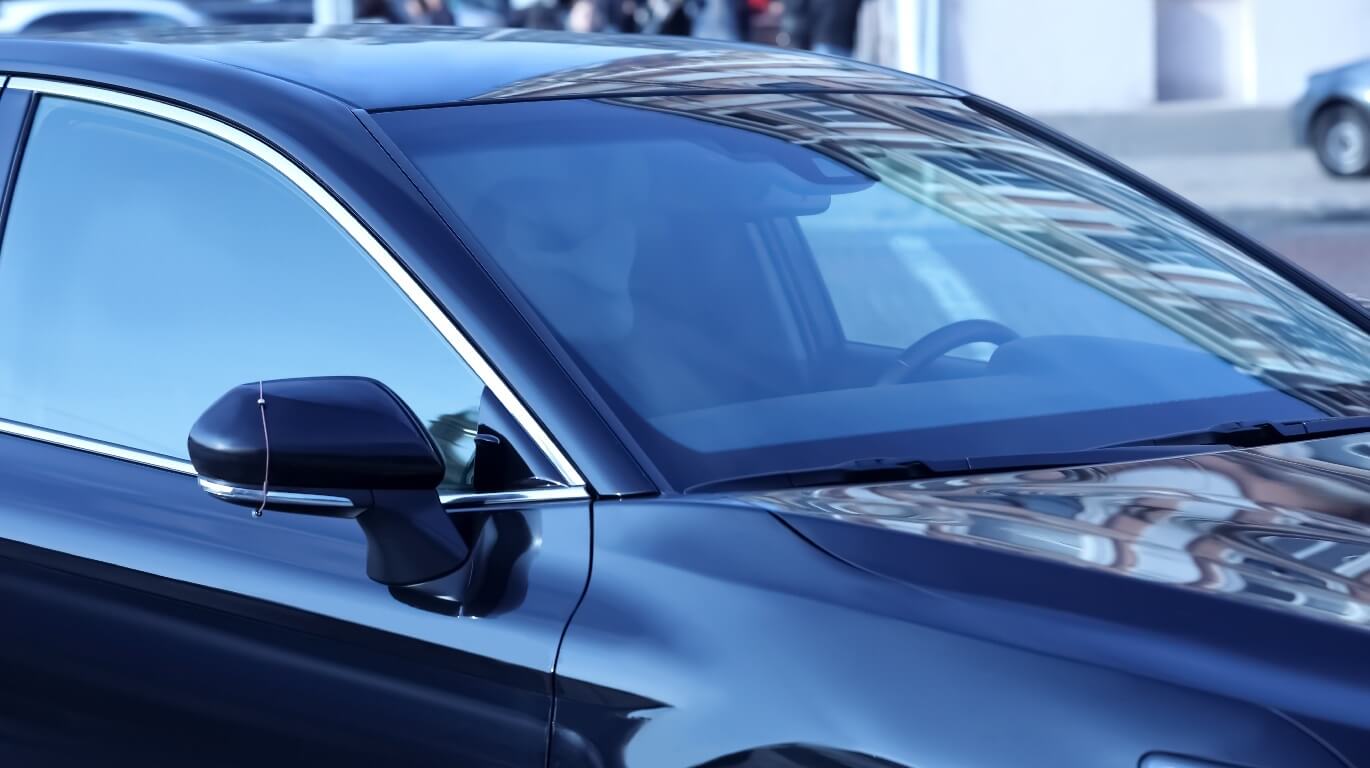
Display cover glass
In-vehicle displays such as CIDs and clusters are getting larger and more complex every year. Due to its strength and workability, glanova® is widely used in the automotive and electronic device manufacturing industries in Japan and overseas.
For document download, click here:Proposal for the use of Automotive Interior

Solar panel
Taking advantage of its thinness, lightness, high strength, and high transmittance, glanova® maximizes the performance of solar cells. We have experience in mass production of perovskite solar cell modules.

Automotive glass
Used as laminated glass for automobiles, it greatly contributes to the weight reduction and fuel efficiency improvement of automobiles.

AR glasses, VR goggles
Highly rated for its high transmittance, it is also widely used in wearable devices.

Others/Cover glass
Wearable watches, smartphones, tablets, computers, etc.
It can also be used as a cover glass for parts other than touch panels and monitors.
For document download, click here:Proposal for the use of OGS
For document download, click here:Proposal for the use of Automotive Interior


Glossary
CS : Compressive stress (surface compressive stress)
A numerical value that indicates the magnitude of compressive stress that appears on the glass surface. The larger the number, the more it prevents the development of microcracks on the glass surface that cause breakage.
DOL : Depth of Layer
A value that indicates the depth of ion exchange from the glass surface due to chemical strengthening.
Aluminosilicate glass
Glass made mainly from aluminosilicate. Compared to soda-lime glass, it has higher chemical durability and is characterized by being more likely to exhibit the effects of chemical strengthening.
Softening point
The temperature at which a substance softens and begins to deform under its own weight. When bending glass, it must be heated to its softening point.
Chemical strengthening processing
By ion exchange, a compression layer is formed on the surface of the thin sheet glass, making it five times stronger than ordinary glass of the same thickness.
CIDs
A CID (Center Information Display) is an information display such as a car navigation system placed in front of the driver's seat of a car.
Cluster
A cluster is a collection of various meters placed in front of the driver's seat of a car.
In a similar sense, it is also called a "meter cluster" or "center cluster".
AG
AG (Anti-Glare) coating is called anti-glare (anti-glare) processing.
This is a technology that provides a function to reduce image reflection, and is a process applied mainly to the surface of display glass.
DS-AG
An abbreviation for Down Stream Anti-Glare, it refers to NSG's proprietary AG processing (anti-glare processing).
Gross
This is a numerical value that expresses the anti-glare property against reflection on the glass surface.
The lower the value, the less reflection, and the higher the value, the more glossy the surface.
Haze
A numerical value that indicates the degree of cloudiness of the display. The lower the value, the more the white cloudiness is suppressed.
White cloudiness tends to occur when the dimple size is 3 μm or less.
Dimple
It refers to the irregular islands formed on the glass surface by the coating process.
AF
It means AF (Anti-Fingerprint) coating, which prevents fingerprints and water/oil stains by making the glass surface water-repellent.
FAQ
Is it possible to send a sample?
Is possible. Please contact us for specifications such as dimensions and thickness.
Contact usWhat is the product size?
Since it will be sold as a raw plate, it can also be manufactured in a customer-specific size. Please contact us with your desired product size.
Contact usWhat is the thickness lineup?
We will consult with you according to your request within the range of 0.33 to 2.0 mm.
Can you process and sell?
Basically, we sell raw plates, but we also sell processed products that have been cut and strengthened. Please feel free to contact us.
Contact usCan you do various coatings?
It is also possible to support film formation and coating on glanova®. Please contact us for details.
Contact usWhat is the price and delivery time?
Please contact us for details.
Contact usDocument download















