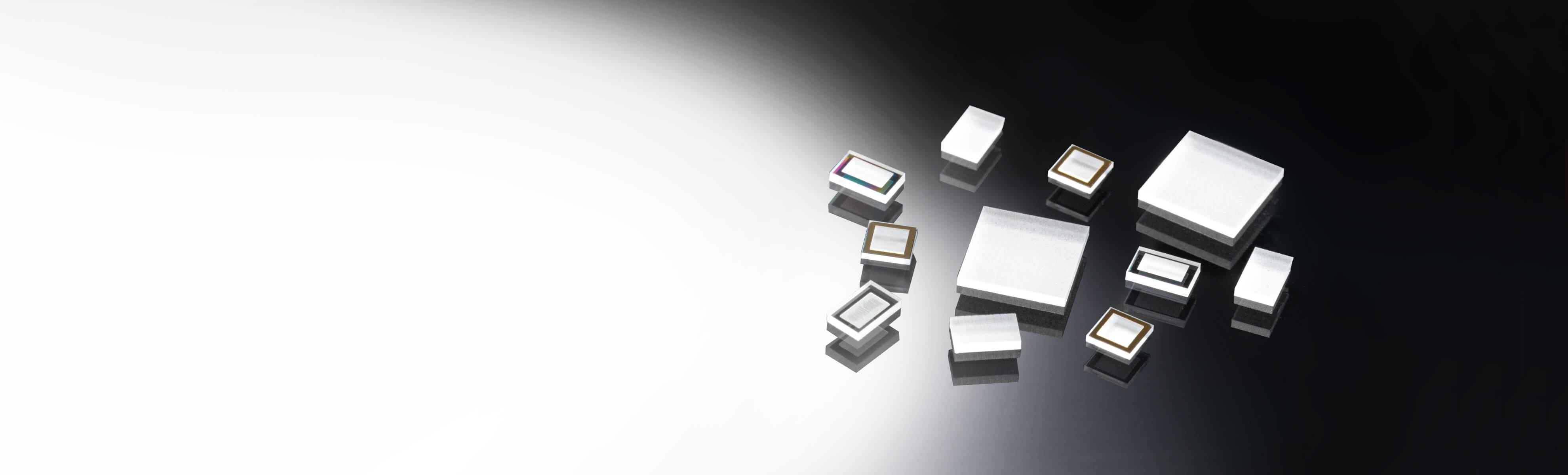
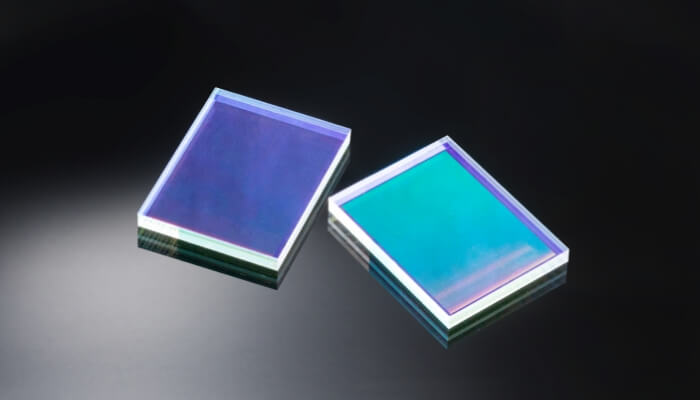
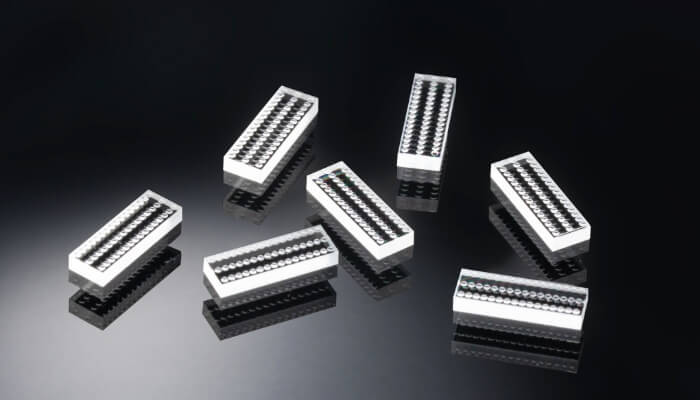
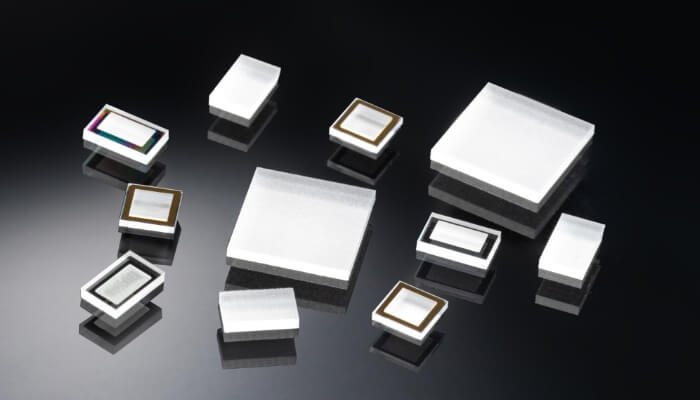
Diffuser
High performance light diffusers are used for security purpose such as security camera our facial recognition, for automatic driving of cars and drones and for 3D sensing using near-infrared light.



Product summary
The unique light diffuser of NSG controls light diffusion in wide wavelength range, from ultraviolet light to near-infrared light. By controlling the microstructure of microlens array formed on a glass substrate, we are capable of providing light diffusers with various patterns, including circle, rectangle and line, and with various diffusion angles.
Moreover, by combining light diffusers with lenses, it is possible to form a super-wide angle light diffusion unit up to 180°. As they are light diffusers that utilize refraction of light by microlens, they achieve high transmittance and stable light diffusion performance.
Through the precision imprinting technology, organic–inorganic hybrid material (high thermal resistance material), and optical design technology, we can design and produce customized light diffuser according to customized requirements.
High performance microlens-type light diffuser
It is a type of light diffuser where numerous microlenses are placed on the surface of glass substrate. As it diffuses light through refraction effect, it can achieve high transmittance. By controlling the shape of each microlens, diverse diffusion patterns can be achieved. Moreover, by optimizing the arrangement of microlenses, occurrence of unnecessary interference fringes and bright spots is prevented.
It is ideal for light distribution control of light sources for security cameras or Time of Flight (ToF) cameras.
Appearance of diffuser
The organic‐inorganic hybrid material is used for the lens material.
NSG’s unique organic‐inorganic hybrid material is used to form lenses on the glass substrate. It has high transmittance in wide wavelength range from visible to near-infrared light, and it has high adhesion to the glass. The heat resistance temperature of the lens material is more than 300℃. Thus, the common solder reflow process can be applied to it.
Benefits of the imprinting technology
As it is produced through the imprinting technology (embossing), it has good morphological stability, and by joining molds, it can be applied to large surfaces. Conversely, when producing small light diffusers, it is possible to first produce them in a batch on a large substrate and then cut it into chips. Imprinting is regarded as a technology suitable for mass production.
In addition, antireflection (AR) coating or metallization of periphery are also possible. Please make an inquiry for details.

Examples of light diffusion property
Required illumination shape, diffusion angle, and intensity distribution are different depending on the purpose. (For instance in the case of diffuser for ToF camera, the area to be photographed is commonly rectangular, and the camera’s angle of view and the lighting’s angle of view must be synchronized. Moreover, as the sensitivity of the sensor, including the lens, changes according to the incidence angle, the strength distribution of the lighting must be adjusted to compensate these changes.)
The microlens-type light diffuser can achieve diverse diffusion properties by controlling the lens shape and lens arrangement.
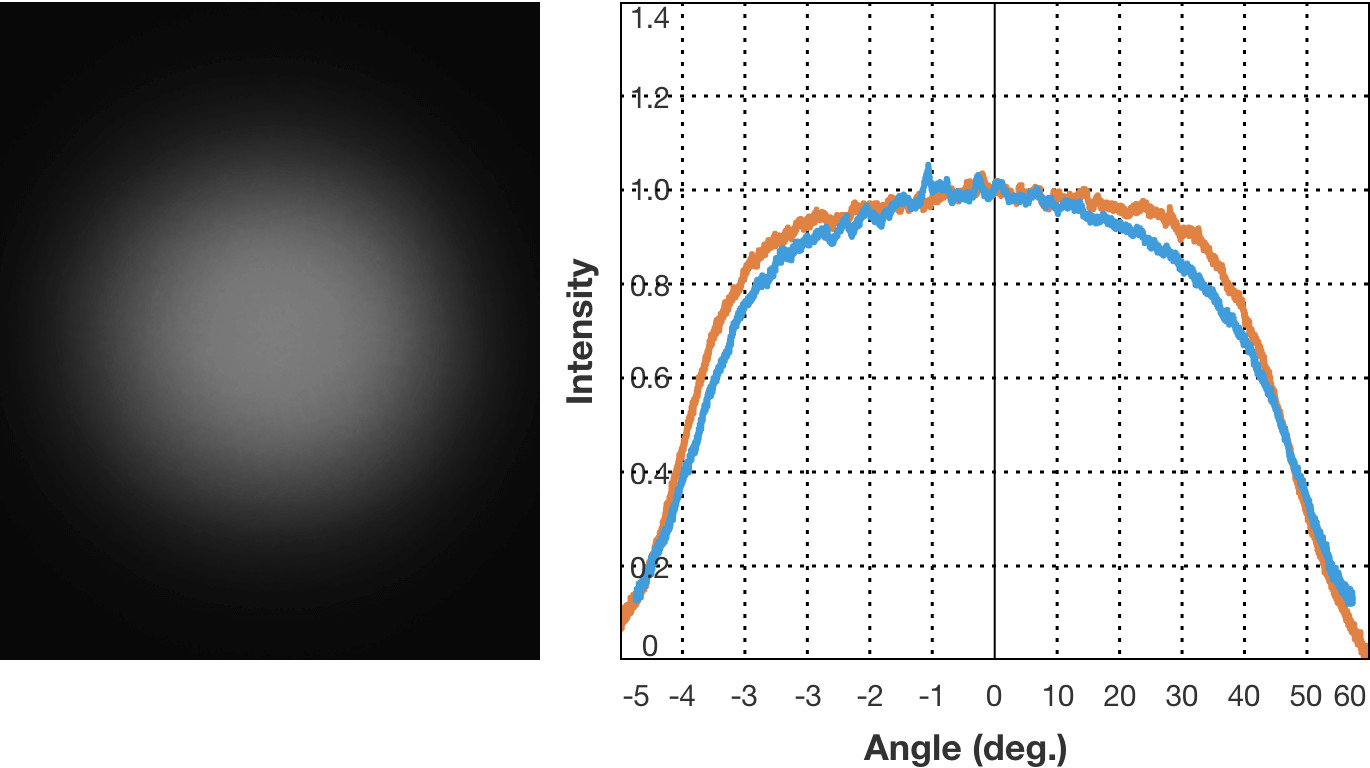
Examples of diffusion pattern. (1) Circle Φ95 degree, flat top
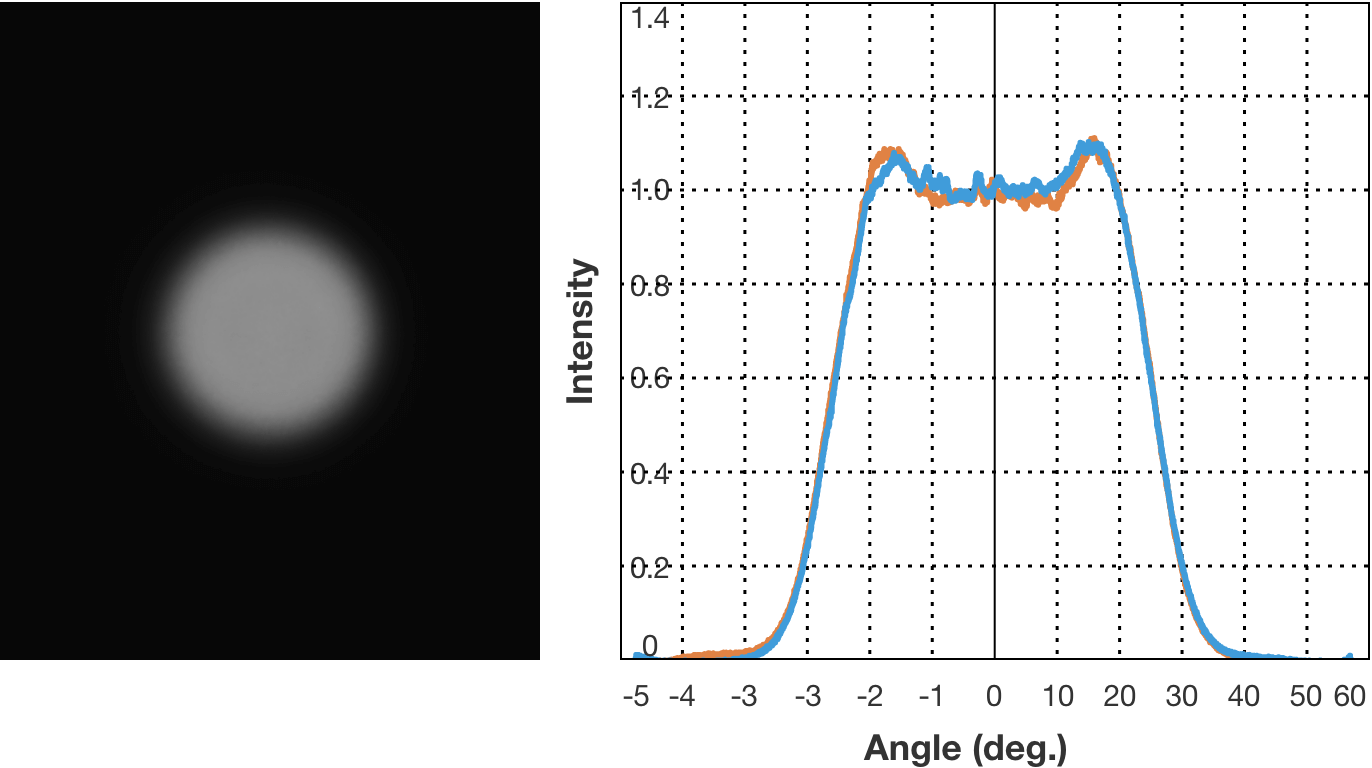
Examples of diffusion pattern. (2) Circle Φ50 degree, batwing
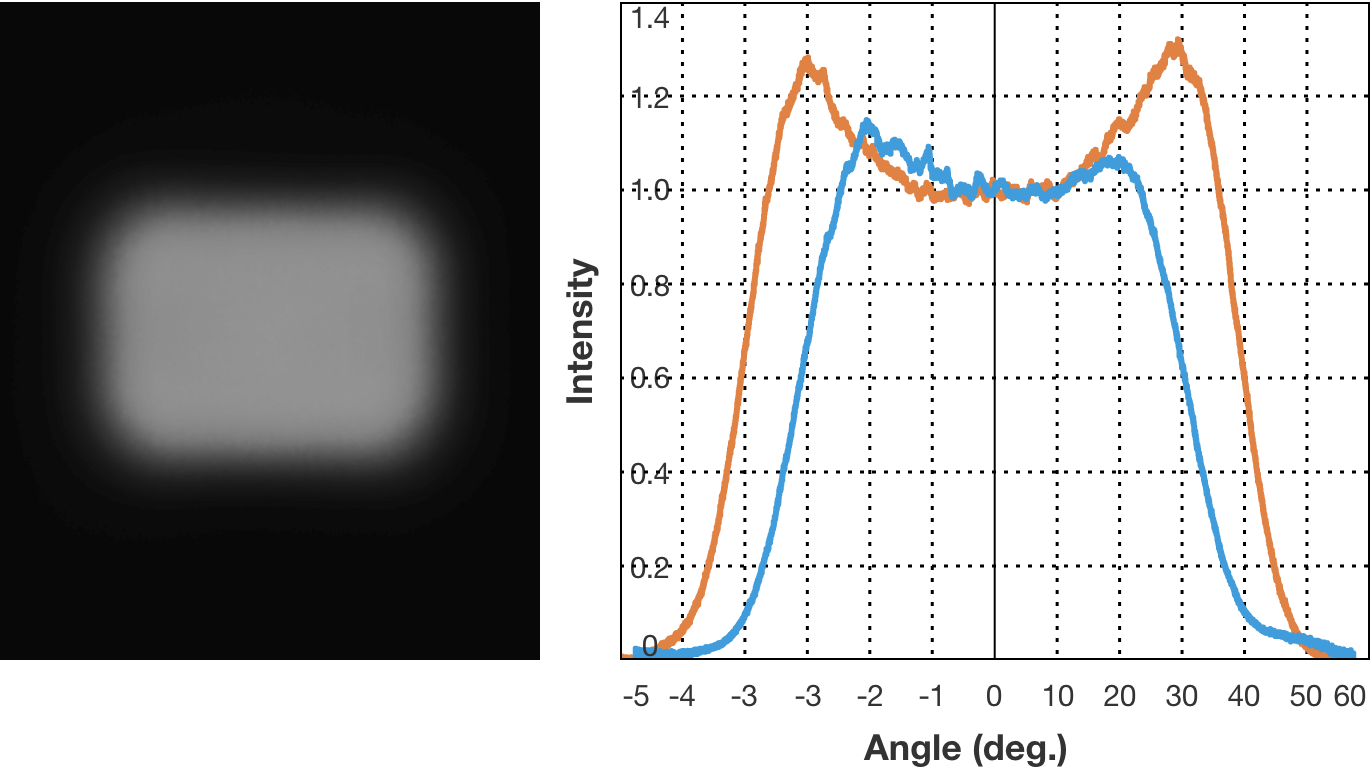
Examples of diffusion pattern. (3) Rectangle 82x64 degrees, batwing
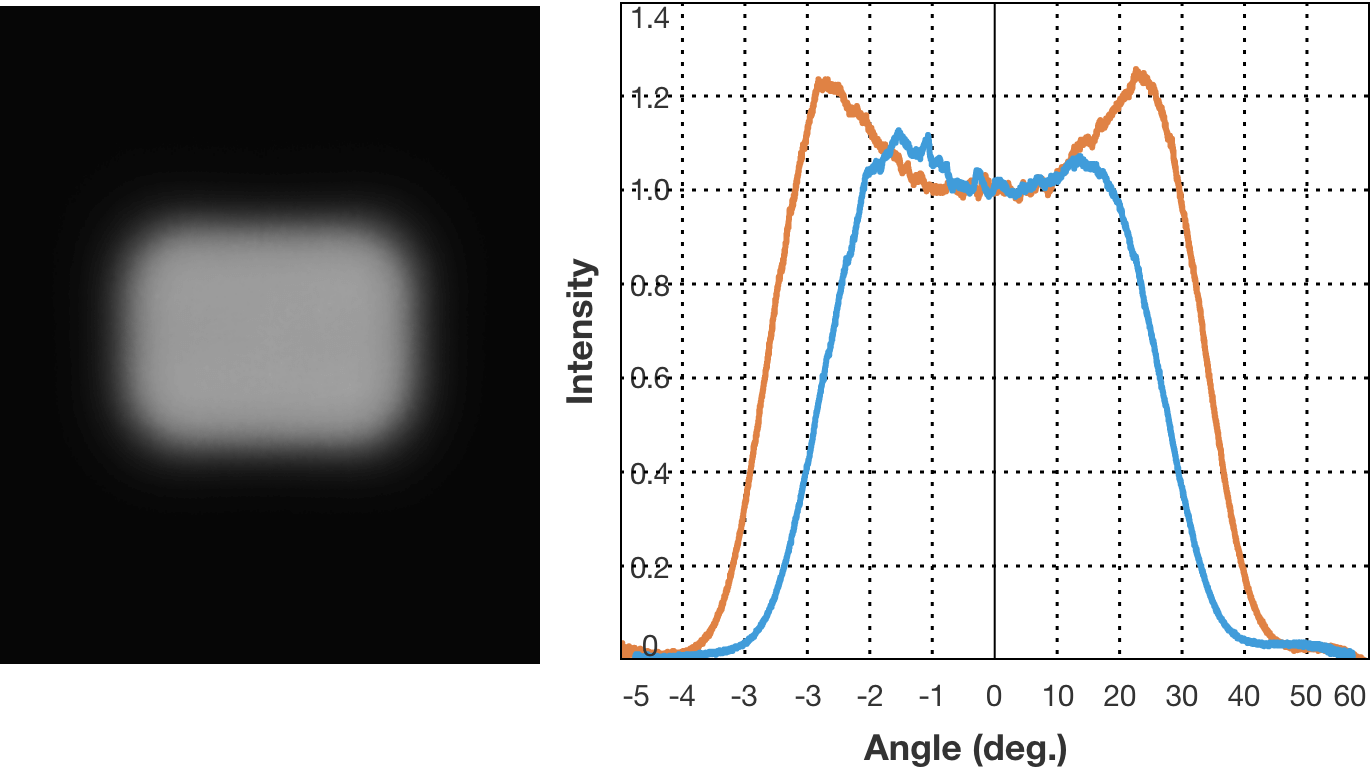
Examples of diffusion pattern. (4) Rectangle 72x56 degrees, batwing
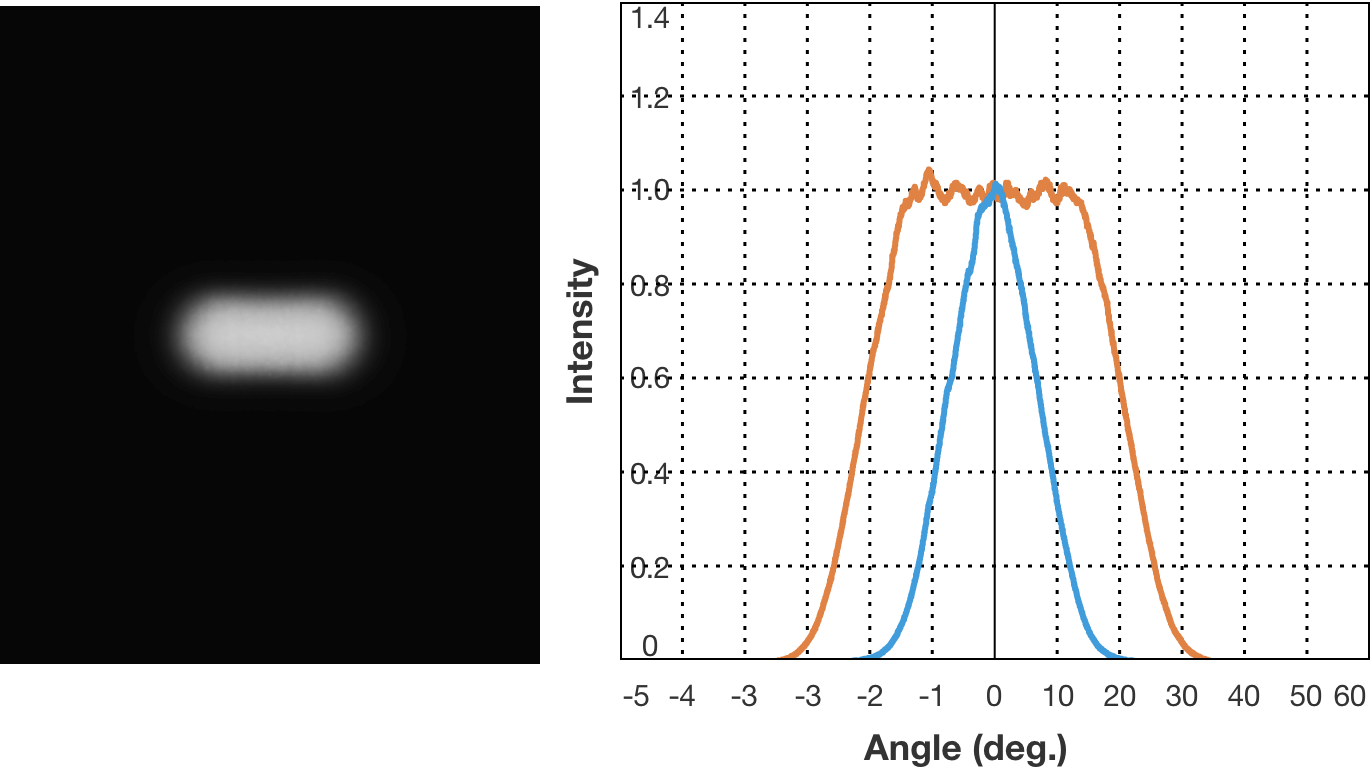
Examples of diffusion pattern. (5) Rectangle 44x16 degrees, batwing
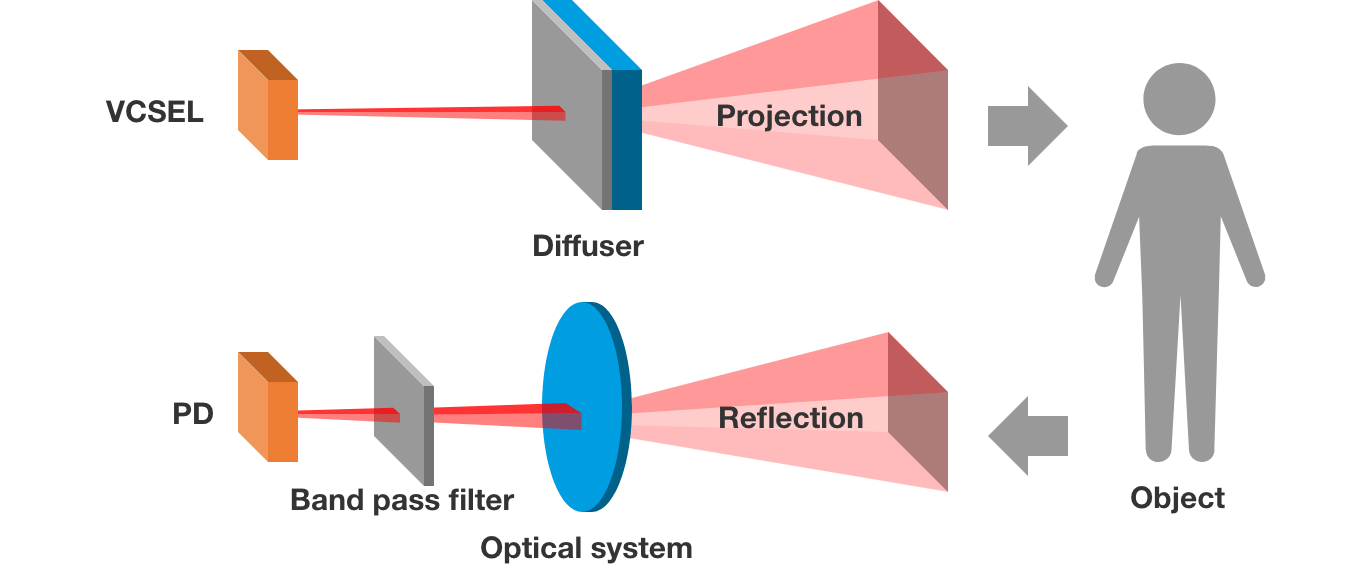
Lighting system for Time of Flight (ToF) camera
Time of Flight (ToF) camera is a type of camera that measures the distance to the subject from the time it takes for the light emitted from the device to hit the subject and then return to the device. The lighting system used for this purpose is required to illuminate the measurement range (inside the camera’s angle of view) as evenly and brightly as possible. As the radiation angle of the light source (commonly, laser is used) is between a few degrees to 20° and it cannot cover the entirety of the camera’s angle of view as it is. By putting the laser beam through the diffuser, the light is expanded until it reaches the required radiation angle and it becomes possible to measure every distance within the camera’s angle of view, which improves the detection accuracy.
Measurement principle of ToF camera: Distance is obtained from the time it takes for the light to hit the subject and then return to the source.
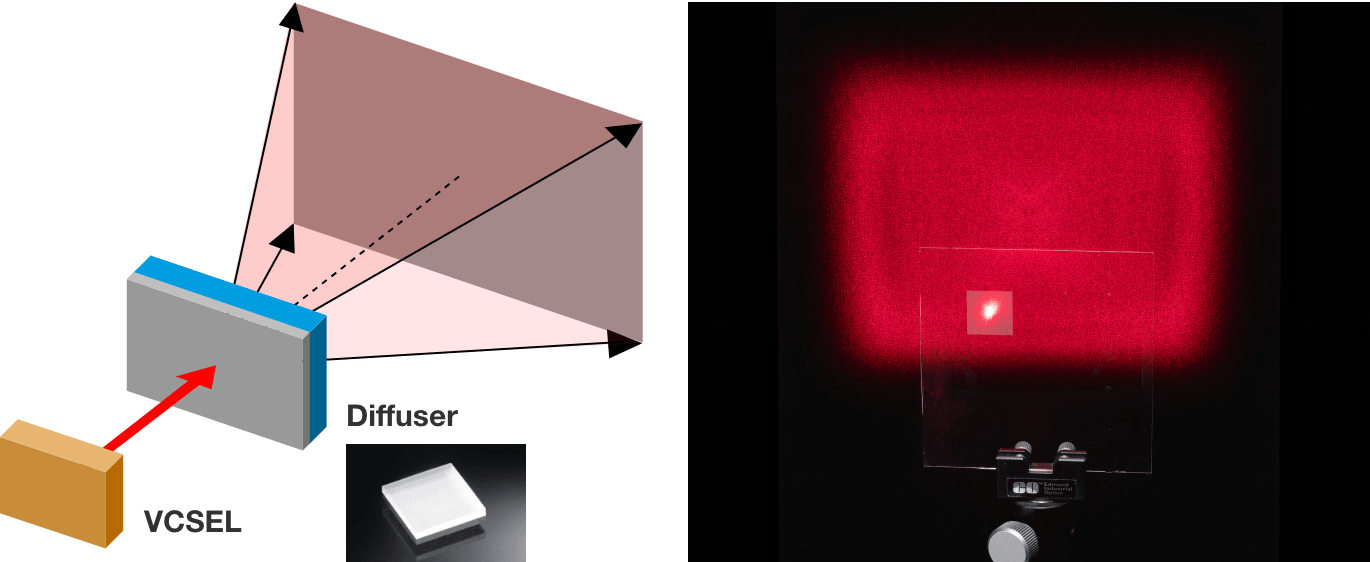
By diffusing light with strong directionality, such as laser beam, using the diffuser, it becomes possible to convert it into a type of light that evenly illuminate the desired area.
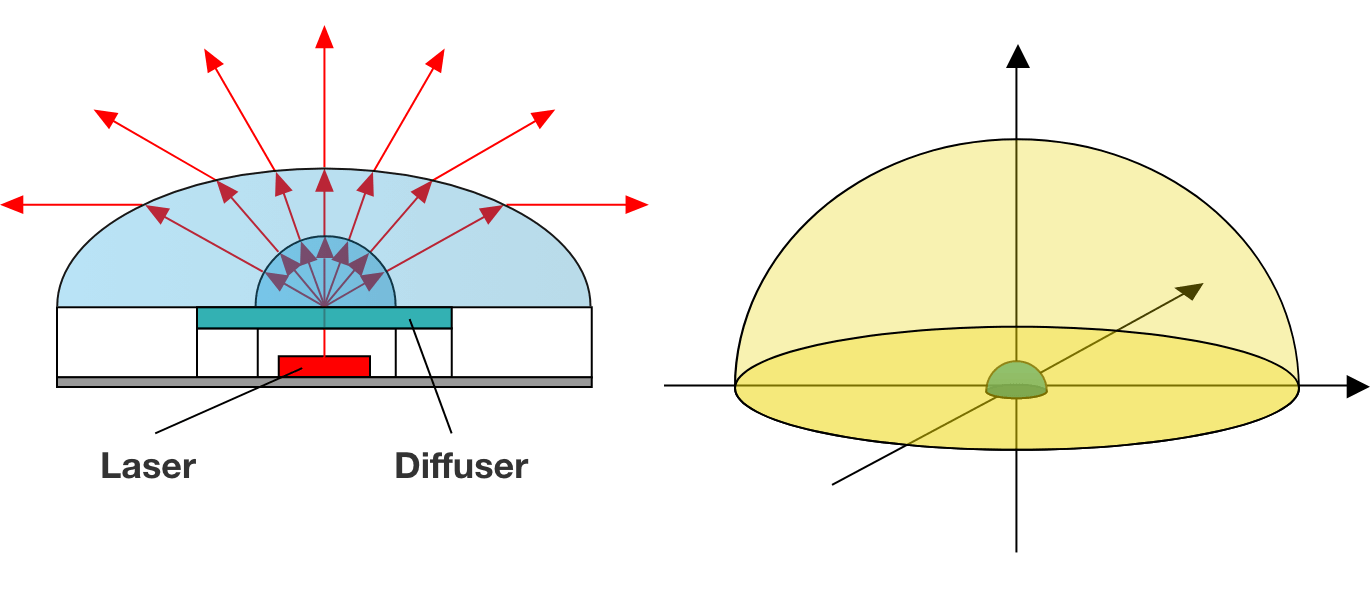
Super-wide angle lighting unit
By unifying the light diffuser and meniscus lens, it is possible to compose a super-wide angle lighting unit whose diffusion angle is more than 180 degrees. It is effective for purposes that require illumination of a wide area such as security camera or car passenger monitoring.

Lighting unit cross section /180 degrees wide angle
Demonstration with a laser pointer
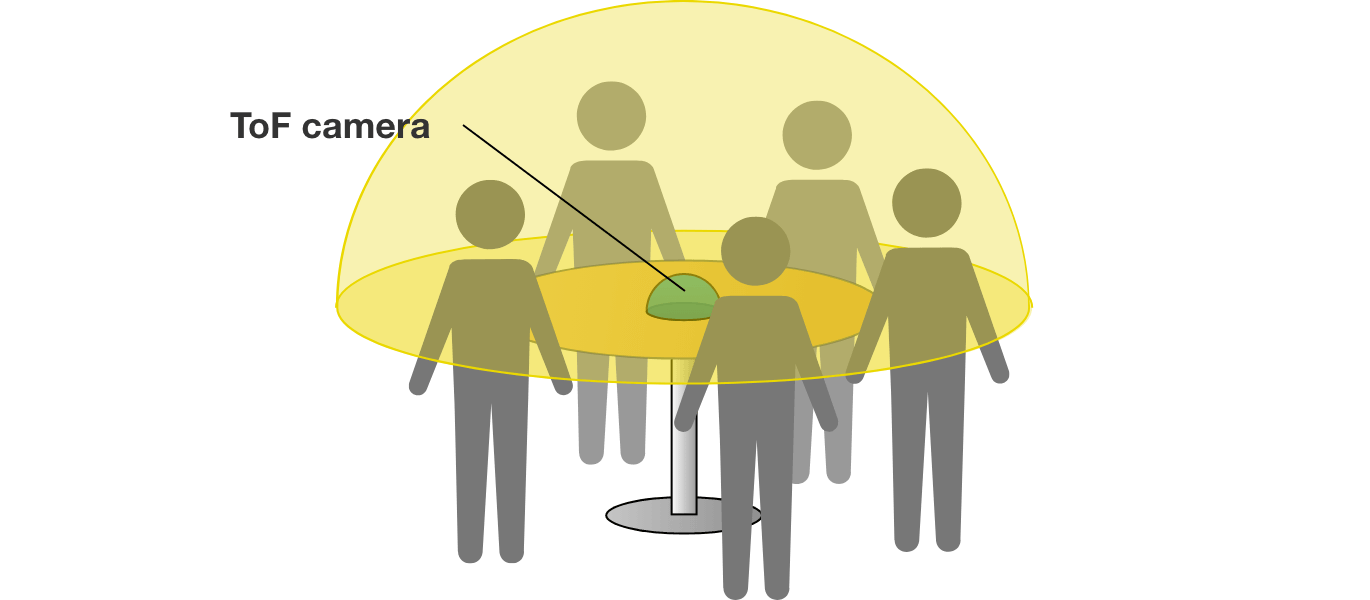
Application example: Image of the distance photographed in 180 degrees wide angle in combination with a ToF camera
Glossary
Diffusing plate (Light diffuser)
It is an optical element for scattering light. For instance, by putting light with high directionality such as laser and LED through a diffuser, they can be turned into diffused light. It is widely used for the backlight of LED light and displays or for sensors.
Diffusion angle
The double of an angle where the strength of the light emitted perpendicularly to the diffuser becomes 1/2 or 1/e is called the diffusion angle. It numerically represents how much a diffuser can widen the light. While the angle of a diffuser does not change when the light entering is not a parallel light (for instance light with diffusion such as LED), the inclination of the light strength near the diffusion angle changes.
Light distribution curve
The curve that represents the direction of light radiation and its strength is called the light distribution curve. There are cases where the horizontal axis represents the radiation angle and the vertical axis represent light strength, and cases where the direction and strength of the light emitted from the center, which is the light source, are represented by vector. The type where the light strength is constant regardless of the radiation angle is known as the flat top characteristics, and the type where light strength increases along with the increase in radiation angle is known as the batwing characteristics.
Illuminance
The amount of luminous flux that enters per unit area is known as illuminance. Its unit is lux (lx).
Luminance
The amount of luminous flux emitted per unit area and unit solid angle from a surface light source is known as luminance. For instance, in an ideal diffusion area known as Lambertian, the luminance is constant regardless of the angle of observation.
Luminosity
The amount of luminous flux emitted within the unit solid angle is known as luminosity. Its unit is candela (cd).
Radiant intensity
The energy emitted within the unit solid angle. Its unit is watt/steradian (W/Sr).
ToF camera
A camera that is capable of capturing depth map by utilizing the principle of ToF (Time of Flight; measurement of the distance to a subject from the time where emitted light hits the subject and then returns). It is widely used in various situations, including measurement inside and outside an automobile and population flow measurement.
VCSEL (Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Laser)
The Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Laser (VCSEL) is a type of semiconductor laser. It characteristically emits light vertically from the substrate surface. It is widely used in optical communication, laser printer, etc. In recent years, it is often used as the light source for smartphone’s facial recognition or as the light source for ToF camera.
Microlens
Lenses whose diameter is between a few micron (μm) to a few hundred μm are known as microlens. They are produced by using molds made of resin or glass. They are used for optical coupling between optical fibers and optical elements or for light diffusers.
Meniscus lens
A lens that is convex on one side and concave on the other. Depending on the difference in curvature of each side, it can behave as a convex lens or as a concave lens. By using concave meniscus lens, it is possible to further widen the light widened by the diffuser evenly.
Directionality
The property where light strength is different depending on the direction is known as directionality. For instance, a laser pointer has good directionality and its light progresses with hardly any diffusion. Light sources without, or low, directionality include incandescent light bulb and fluorescent light. Depending on the purpose, light with directionality or those without directionality are used.
FAQ
What is the heat resistant temperature?
It can be used under the normal reflow conditions. It can be used for up to 330℃ (three minutes, in nitrogen atmosphere) reflow.
What is the largest diffusion angle?
The maximum diffusion angle of the light diffuser alone is 120 degrees. When combined with lenses, light can be widened up to more than 180 degrees.
What are the specifications of the standard product?
Some examples are listed on our website. Please check the website.
Can you supply samples?
Yes. In addition to the standard products, we can supply samples of other products if there are stocks. Please make an inquiry.
Contact usCan you adjust light distribution control?
We can design for almost any type of light distribution control. We can also adjust the shape of the pattern into various shapes, including circle, rectangle and oval.
Can you produce an entirely inorganic diffuser?
It is possible. Entirely inorganic diffusers are produced through the sol–gel technology and they are suitable for purposes that require particularly good thermal resistance or high ultraviolet transmittance.
How long does it take to design a customized product and produce its prototype?
The lead-time is between one and half months and two months, including the design.
How much does prototype production cost?
It depends on the specifications. Please make an inquiry.
Contact usWhat are the points of caution upon its usage?
As the surface of a diffuser is composed of tiny lenses in micrometer scale, please do not scratch the surface with force.
As the light is widened through the refraction effect of the microlens surface, the diffusion property changes when substances with different refractive index such as liquid is on the surface. Please make sure that water or glue is not on the surface.
The diffuser has the front side (where the microlenses are arranged) and the back side (flat side). Please make sure that the diffusion side is facing the light source when you are using it. (While the light is diffused when the back side is facing the light source, the resulting diffusion strength distribution does not follow the design. This difference becomes more pronounced with diffusers with larger diffusion angle. Please make sure to use the right side.)
What happens when the light enters with a slant?
The diffuser is designed with the light entering perpendicularly to the substrate in mind. When light enters with a slant, the light distribution control and the diffusion pattern shape become asymmetrical. For instance, when slanting light enters a diffuser that diffuses light in rectangle pattern, the diffusion pattern becomes trapezoid.
What is the thickness of the diffuser?
Normally, it is about 0.5mmt. However, it can be changed to thickness between 0.2mmt and 1mmt.










