Anti-fogging Coating
The thin film coating technology of NSG is comprised of proprietary sol–gel and hybrid technologies, which combine organic and inorganic materials, and this is used for solving problems and improving the reliability of camera modules (CCM).



Product summary
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS), monitoring systems, and individual authentication systems are required to collect image information accurately by camera modules (CCM) and image sensors (CCD, CMOS), without impacted by changes in the environment (humidity, temperature, rainfall, and backlighting). The surface (inner surface) of the cover glass/lens may become foggy when temperature differs between outside and inside of CCM cover glass/lens or sudden change in air pressure. The antifoggging coating provided by NSG has excellent transmission characteristics, durability, and water resistance. In addition, it improves reliability of in-vehicle, surveillance, and various high-performance cameras, supporting image sensors to capture image information precisely.
Characteristics of Anti-fogging Coating
(1) High adhesiveness to glass and resin substrates
The NSG antifogging coating has a high adhesiveness against glass-based substrates. In addition, antifogging coating for resin-based substrates, such as PEF film, are being developed.

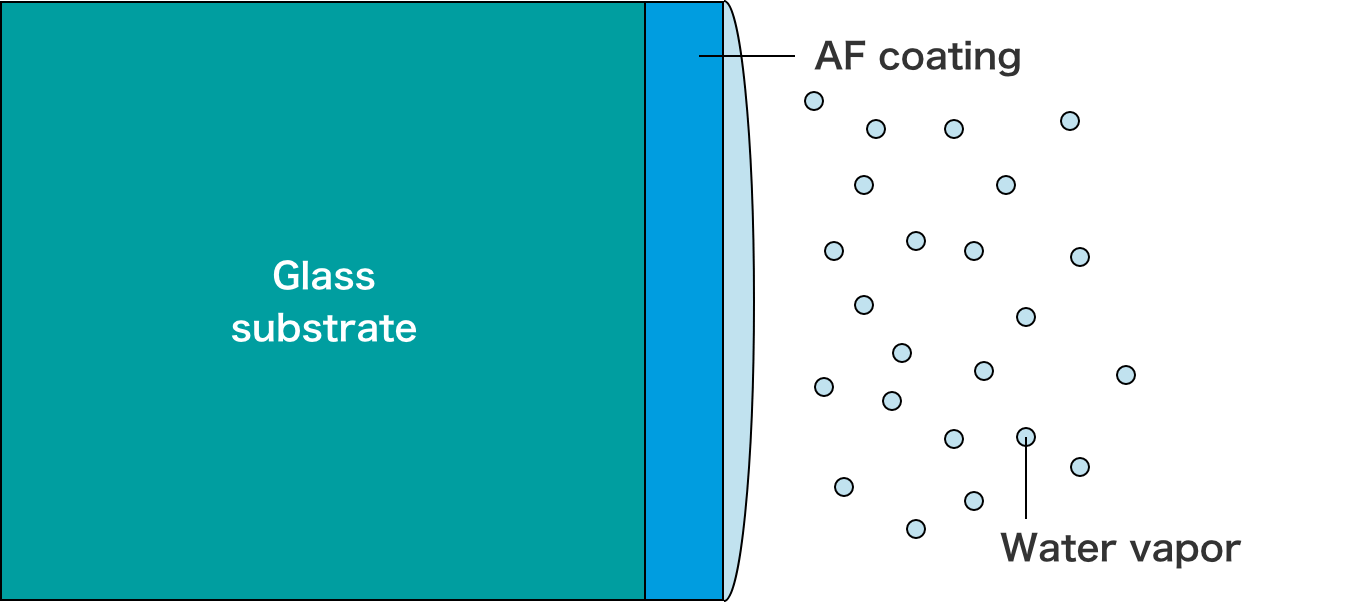
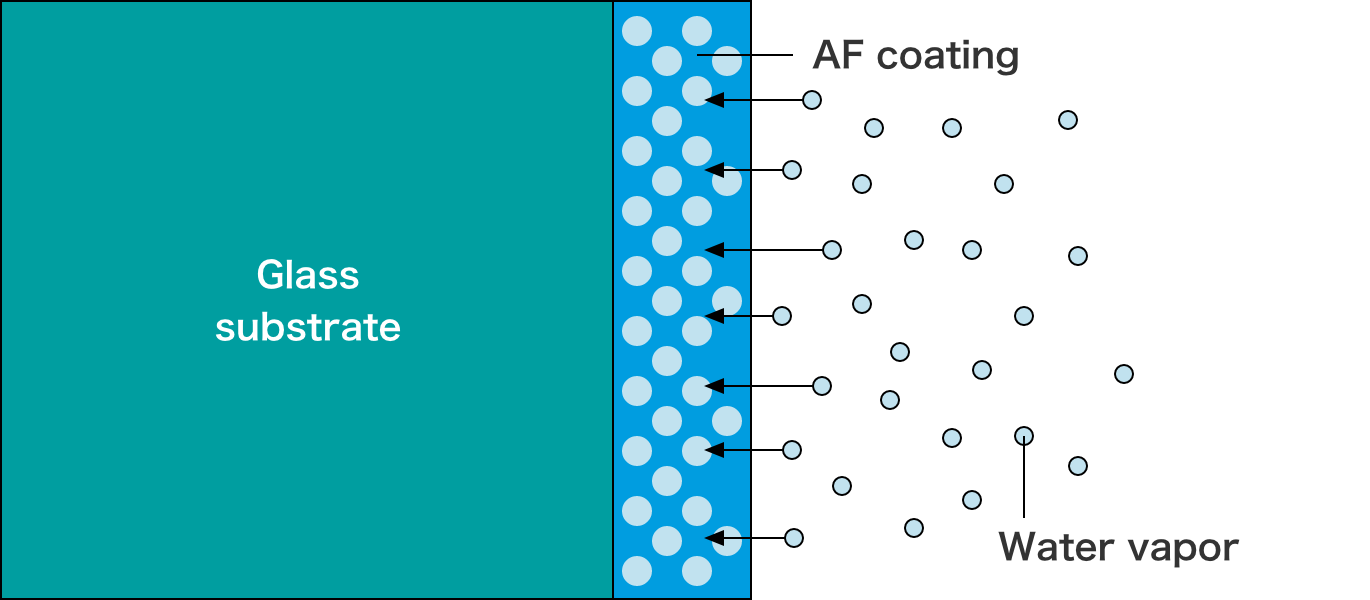
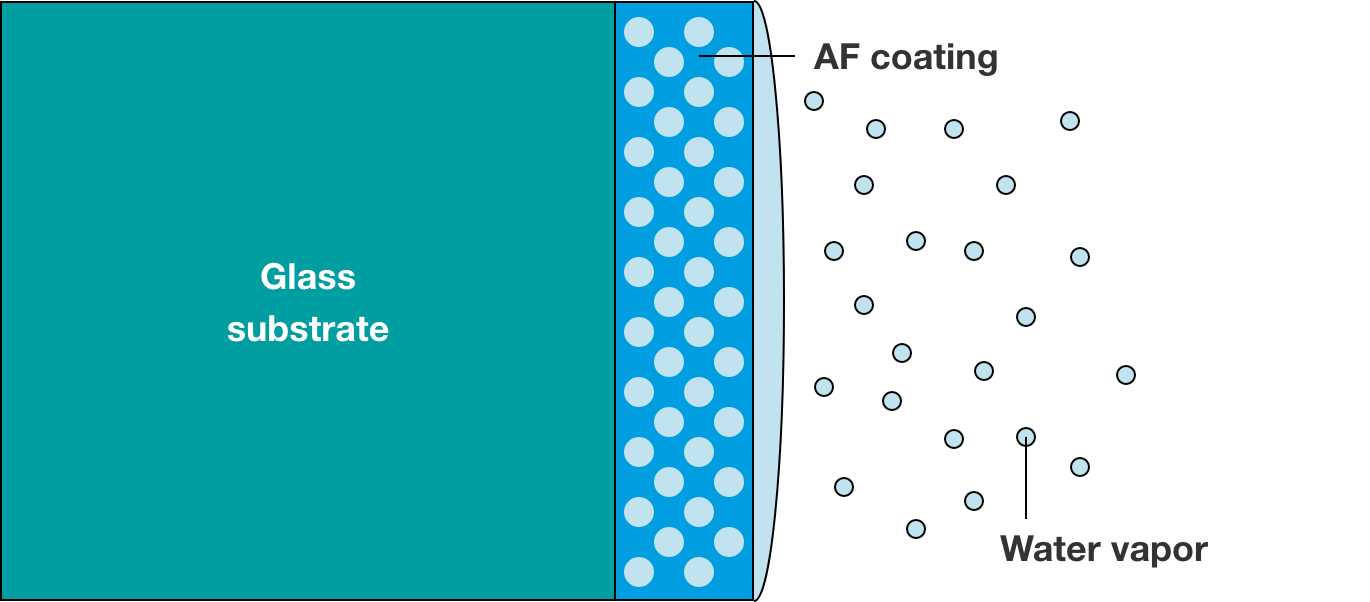
Effect of antifogging coating film (image) Left: Untreated Right: With antifogging coating film

Effect of antifogging coating film (image) Left: Untreated Right: With antifogging coating film
(2) Controls droplet adhesion behavior of cover glass/lens surfaces
By adjusting the structure of the antifogging film, you can control the hydrophilic and the hydrophobic properties of the film surface.
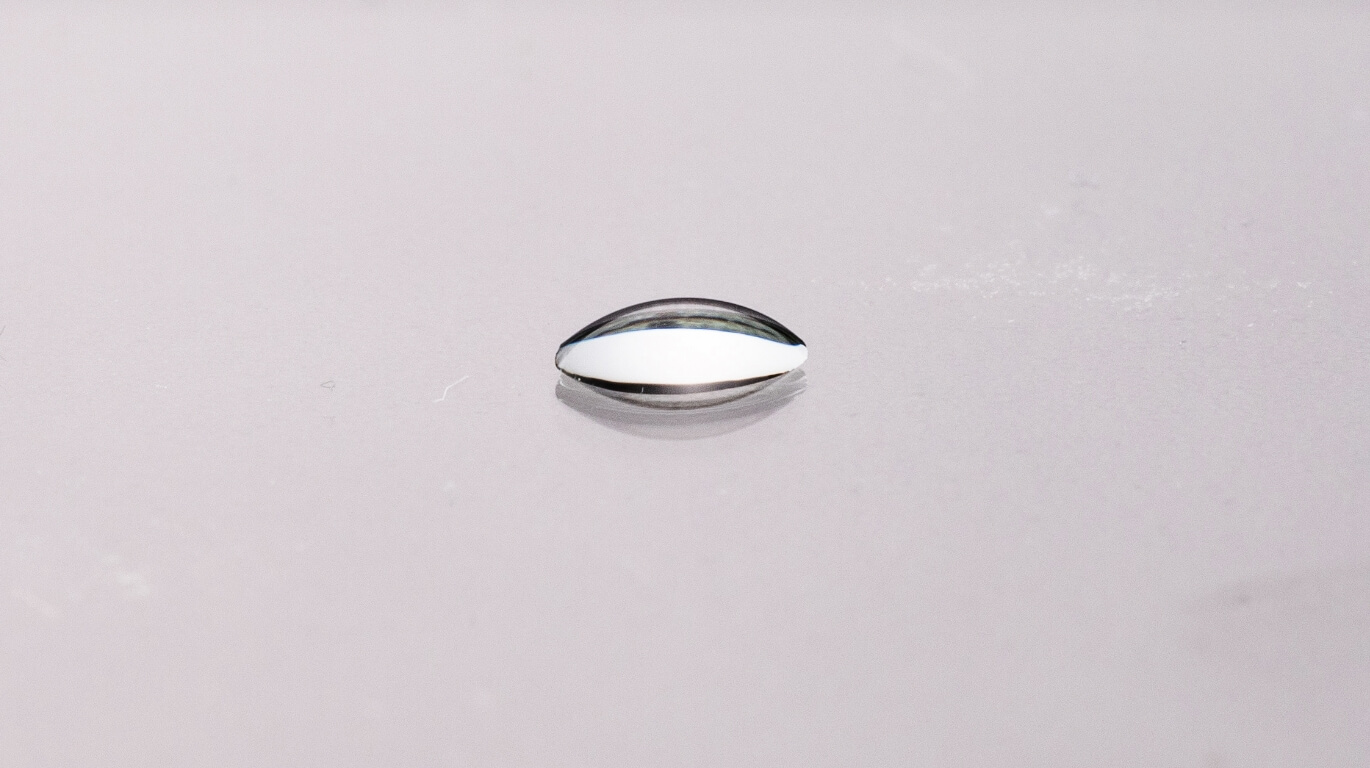

Contact angle against water (Untreated)
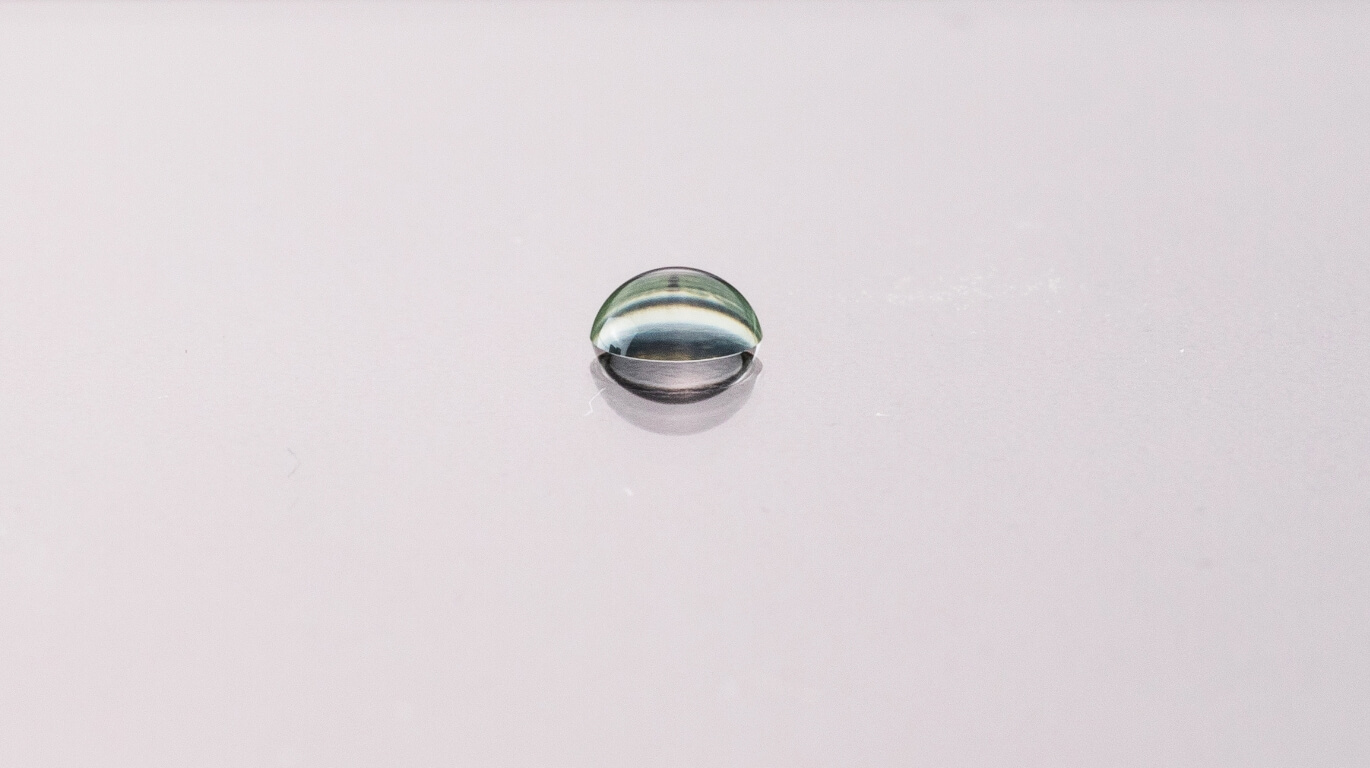

Contact angle against water (With antifogging coating film/Water absorption + water-repellent type)
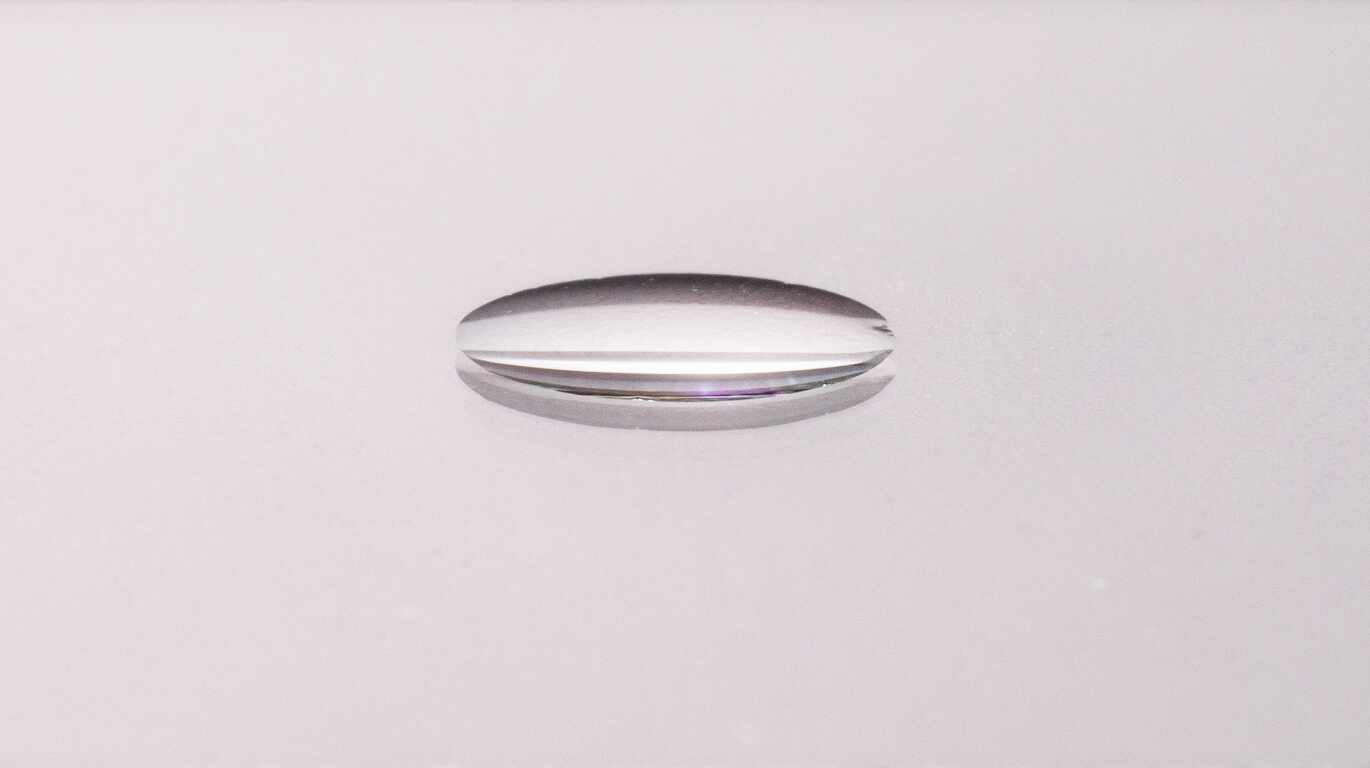

Contact angle against water (With antifogging coating film/Water absorption + hydrophilic type)
A uniform water film is formed on the film surface to maintain visibility.

Relationship between water film formation and visibility Uniform water film formation (visibility: good)

Relationship between water film formation and visibility Partially nonuniform water film formation (visibility: poor)

Relationship between water film formation and visibility Nonuniform water film formation (visibility: poor)
(3) Design of antifogging mechanisms for antifogging coating.
Multiple antifogging mechanisms are available according to the operating environment.
Hydrophilic type
A homogeneous water film is formed on the surface of the coating in response to the changes in temperature and humidity to prevent the fogging of the substrate. This forms a homogeneous water film and maintains visibility even in bad weather. This makes it applicable for use in environments that have comparatively small changes in temperature and humidity.
Water absorption type
This water absorption type absorbs water in the structure of the film to prevent fogging of the substrate. This allows high visibility to be maintained even in everyday-temperature and everyday-humidity environments.
Water absorption + hydrophilic type
The antifog coating has a combination of both hydrophilic and water-absorbing functions. The hydrophilic function maintains high visibility in low to medium humidity environments by absorbing moisture. Meanwhile, in high humidity environments, the water absorbing function forms a water film to maintain visibility. This makes it applicable for use in places where temperature and humidity environments are highly changeable.
Hydrophilic type: Image showing water film formation on the surface of a hydrophilic antifogging coating
Water-absorbing type: Image of water uptake into the antifogging coating
Water absorption + hydrophilic type: Image of water film formation on the surface of an antifogging coating as water is absorbed into the film
Hydrophilic type: A homogeneous water film is formed on the surface of the coating in response to the changes in temperature and humidity to prevent the fogging of the substrate.
Water-absorbing type: In a high-humidity environment, water from the surrounding area is absorbed into the film, and the film becomes foggy when it reaches water adsorption saturation. In a low-humidity environment, the water in the film is released in a short period of time.
Water Absorption + Hydrophilic Type: In high humidity environments, a uniform water film is formed on the surface of the membrane and transparency is maintained.
(4) Water resistance
Antifogging coating, which uses the NSG proprietary sol–gel and hybrid technologies, combines inorganic and organic materials and demonstrates high water resistance.
(5) High transparency
A smooth antifogging coating can be formed that is transparent and has little light scattering, with almost no light absorption in the visible light range.
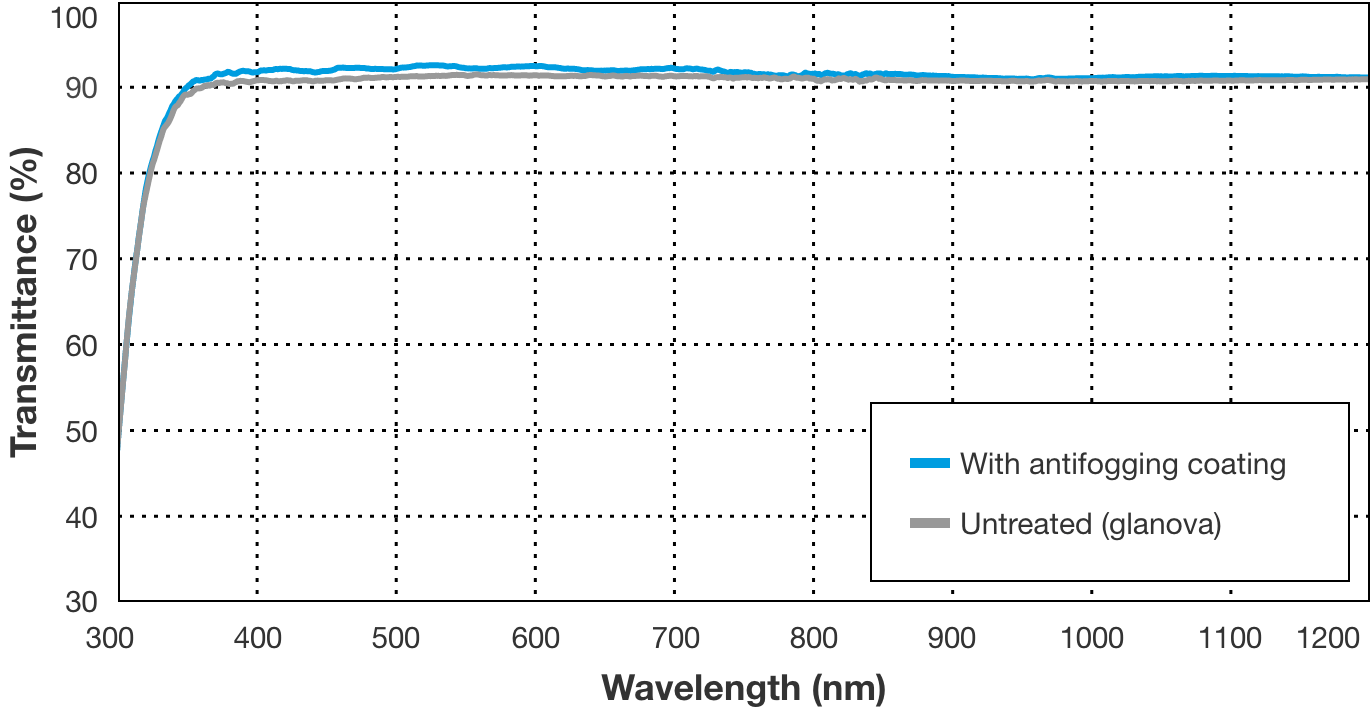
Transmission characteristics
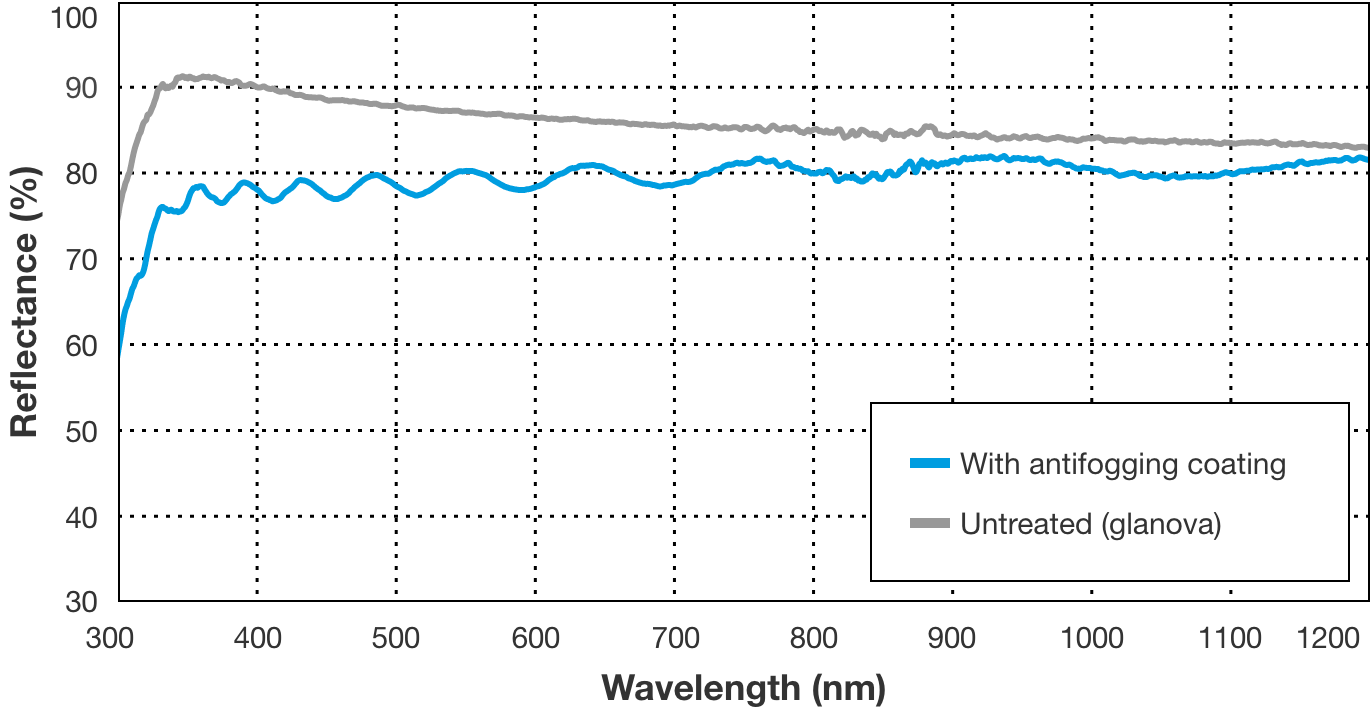
Reflection characteristics
Performance evaluation of antifogging coating
NSG antifogging coatings have mainly been developed to add antifogging properties to glass substrates. In addition, they can be applied to glass substrates for providing durable antifogging protection without compromising the optical properties of the substrate.
Test conditions (NSG test conditions)
(1) Optical performance: Transmittance and reflectance are measured at 550 nm by applying antifogging on a glass substrate.
(2) Adhesion: JIS K 5600 cross–cut test
(3) Antifogging performance: An antifogging film sample is placed on a hot water bath (60°C–90°C) and assessed regarding whether any change occurs in its appearance or fogging properties.
(4) Durability: Antifogging performance is evaluated on samples that have been immersed in pure water for a certain period of time before being air-dried.
(5) Abrasion resistance: Assesses whether there is any change in appearance or fogging properties after rubbing the antifogging coating with a soft cloth.
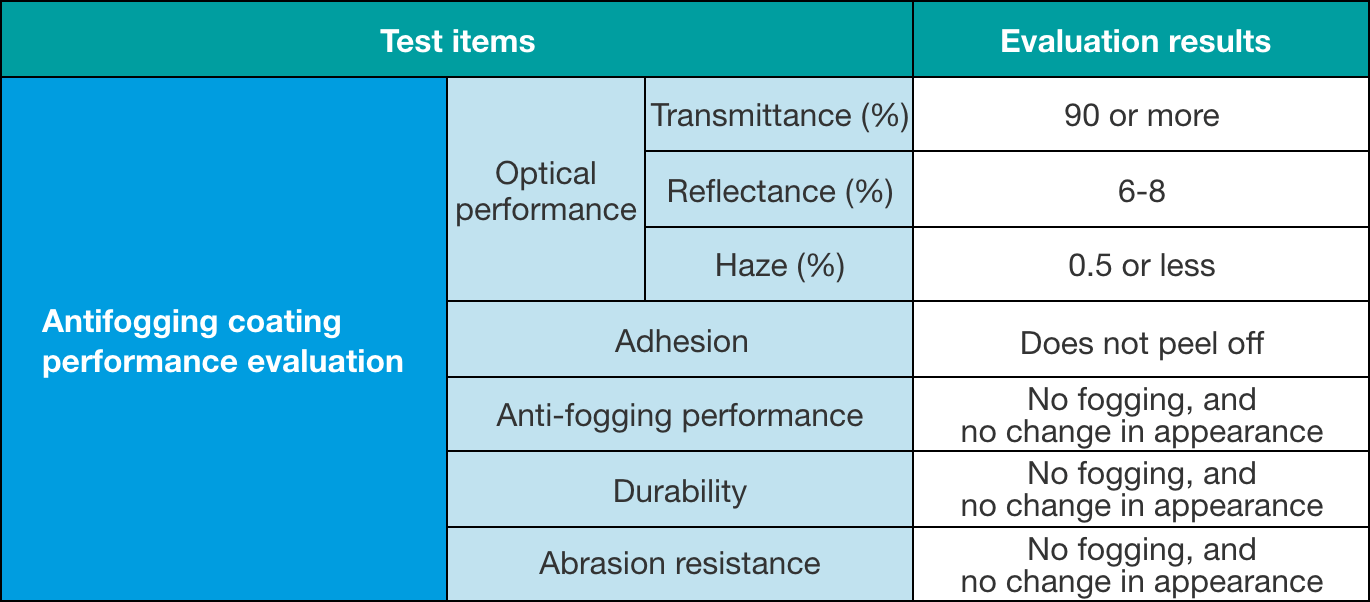
Antifogging performance evaluation results

Antifogging durability test
Proposal for cover glass for a surveillance camera (critical comparison with distributed market product)
Surveillance cameras are installed in a variety of indoor and outdoor locations. They are often used in harsh, outdoor environment, where changes in the surrounding environment (humidity, temperature, rainfall, backlighting) can make it difficult to capture accurate image information. A comparative evaluation of NSG's antifogging coating (coated type) and the antifogging treatment (coated type) used in market surveillance cameras was performed.
(1) Comparison evaluation method
This was a comparison of the antifogging performance, antifogging durability, and wear resistance with antifogging coated cover glass of market surveillance cameras
(2) Evaluation results
NSG's antifogging coating is superior in terms of water durability and abrasion resistance, and shows excellent performance in terms of antifogging durability that is expected in cold areas and coastal regions.
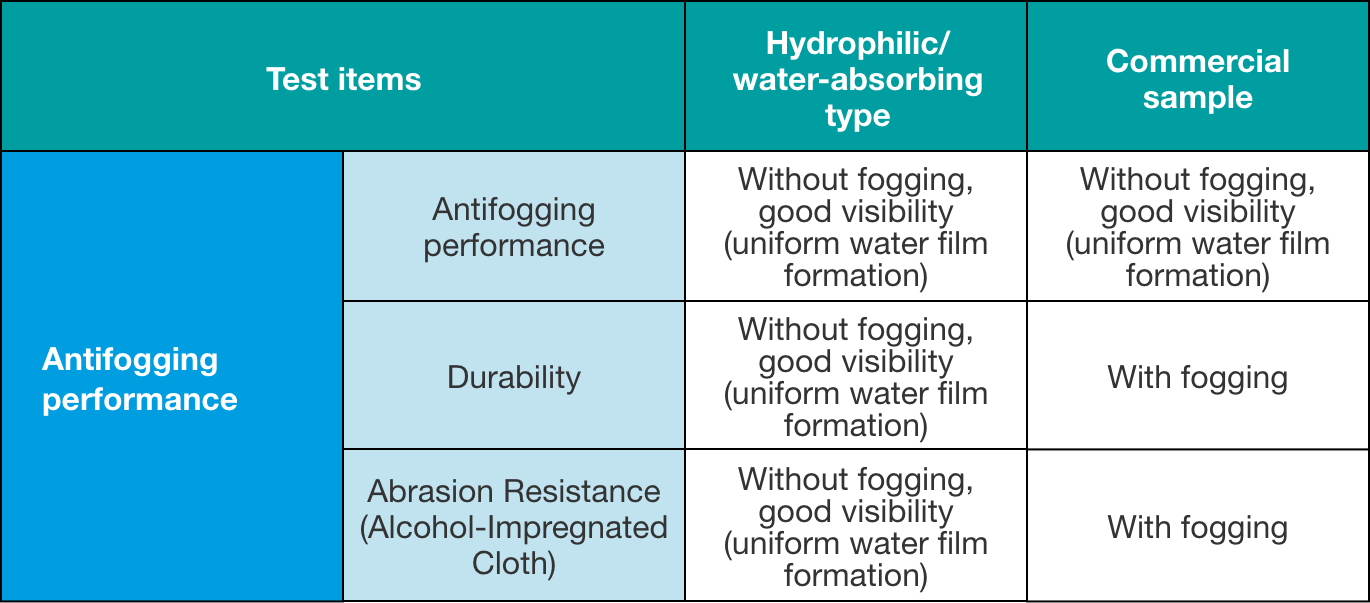
Evaluation results table
Main uses and applications
The NSG antifogging coatings are developed for various applications. Please contact us for more information.

Cover glass applications for surveillance cameras and personal identification system cameras

Cover glass for automotive cameras, ADAS, LiDAR

Lenses for eyeglasses and sports sunglasses

High-performance camera lenses and optical filters

Next-generation mobility applications

Cameras and authentication stems for smartphones and next-generation mobile devices

Headlight applications
Development of antifogging coating used for plastic substrates
The main purpose of the NSG’s development of antifogging coatings is to use with antifogging properties to glass substrates. There is also parallel development taking place for antifogging coatings for plastic substrates (PC and PET resins).
As PC resin, which has excellent optical properties, is an injection molded, it can be used in various optical components, including CCM optical lenses and pickup lenses, surveillance camera cover glass, and automobile headlights, as well as optical lenses for glasses and sunglasses. However, it is also a resin that is difficult to achieve adhesion for surface treatment.
Evaluation Results
The antifogging coating of NSG can be used to form a durable antifogging film on PC sheets.
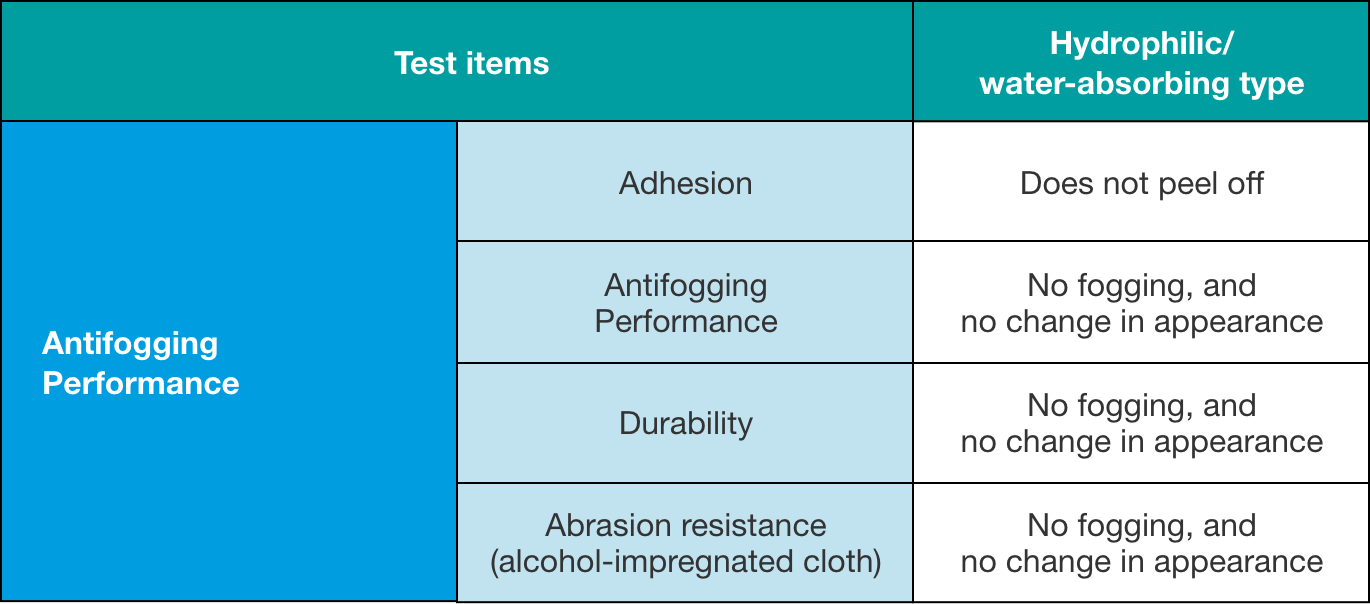
Evaluation Results (PC Resin Substrate)

Antifogging performance (Left: Untreated/Right: With antifogging coating)
Adhesion to PC substrate
Glossary
Antifogging coating
This means that an antifogging coating is attached to cover the surface of the substrate.
Antifogging
Glass and plastic become fogged when the temperature of the surface drops below the dew point and, in this situation, moisture in the air adheres to the surface as fine water droplets. This causes the diffuse reflection of light. By controlling the state of moisture adhesion, light scattering is suppressed, preventing the fogging phenomenon. One example of the antifogging technology is the hydrophilic and water-repellent treatment of material surfaces. Various antifogging technologies have been developed to prevent the fogging of material surfaces.
Visibility
This indicates the degree to which an object can be seen visibly with the eyes. High visibility means the object can be seen in detail.
Exhalation
This refers to expelling air from the lungs through the mouth and out of the body. The antifogging performance can be simply checked by blowing air through the mouth and to see if the antifogged surface becomes foggy.
Advanced Driver Assistance System (ADAS)
ADAS is short for advanced driver-assistance systems. It is a general term used for systems that monitor information about their surroundings, control driving operations, alert the driver, support comfortable driving, and prevent accidents. ADAS is a general term for systems that support comfortable driving and prevent accidents. The system supports "cognitive," "judgmental," and "operational" functions when driving.
Surveillance system
A surveillance camera system does not refer to just one surveillance camera, but instead refers to a system that connects multiple surveillance cameras via a network with the aim of managing and storing video and audio.
With such advances in technology, it is now possible to deal with large amounts of data, and for this, it is better to monitor with a surveillance camera system rather than a single surveillance camera.
Remote monitoring systems and centralized monitoring systems, which are advanced monitoring systems, are being utilized.
Personal authentication
As IT has advanced, we are seeing a rapidly growing need to be able to identify (personally authenticate) users when they use or log into devices or systems. A personal authentication system identifies whether the person attempting to use the device or system is the same person who previously registered. It is possible for companies to handle the private information of people and companies securely using these personal authentication systems. mage data (physical characteristics = fingerprints, face, hand veins, etc.) are often used as means of personal authentication.
Compact Camera module (CCM)
A Compact Camera Module (CCM) is a device for industrial use with a structure similar to that of a consumer-use single-lens reflex camera. A lens and a camera make up this camera module. In the CCM, light entering from the lens is projected on to the photographic element and converted into electrical signals to obtain images. There are two types of camera elements, CCD and CMOS.
Sol–gel technology
The sol–gel method is a method in which starting materials are made out of a solution containing inorganic materials, organometallic salt materials, etc., following which the solution is hydrolyzed and condensed to form a colloidal solution (sol state). Thereafter, the reaction is accelerated to form a solid (gel state). Further, it is heat-treated to produce high-purity glass or ceramics.
Hybrid technology combining inorganic and organic materials
This technology involves combining organic and inorganic materials at the molecular level. This then creates structures (bonded and unbonded) with both organic and inorganic material characteristics.
Light scattering
Light travels straight in an even medium. The direction of light may change, however, if the medium is uneven. In general, we call “light scattering” the phenomenon in which the direction of light travel changes in an irregular manner as a result of small water droplets or fine particles that do not allow light to pass through in the direction of travel.
Spin coating
Spin coating is when a thin film is formed on an object by using a spin coater to put a certain amount of liquid on the top surface of a flat coating object, following which the centrifugal force that can be generated by rotating the object at high speed is used.
Dip coating
Dip coating refers to the formation of a thin film on an object by dipping the object to be coated into a liquid vertically and then adjusting its viscosity, surface tension, gravity (gravity of the flowing down of the adhering liquid) and liquid velocity. This enables the object to be pulled up and coated and the film thickness to be controlled.
Spray coating
In this process, a spray coater is used to form a thin film on an object by atomizing (misting) a liquid and spraying it onto the object to be coated.
Water film formation
This refers to the phenomenon in which a thin layer of water forms on the surface of an object.
Dew point
This is the temperature at which water vapor in the air becomes liquid (fog) after it is cooled. The saturated water vapor content is the limit amount of water vapor that can be contained in the air at a certain temperature, and if that amount (saturation state) of water vapor is exceeded, this appears as fog. The temperature at this time is the dew point (dew point temperature).
Image sensor
The process of capturing images with a digital camera involves converting the light of the subject entering through the lens into digital image data before outputting it. The data is converted in the part known as the image sensor. There are two types of image sensors, CCD (Charge Coupled Devices) and CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor). The elements that make up a CCD image sensor can be broadly classified into a light collecting lens, a color filter, a photodiode (light receiving element), and a transfer circuit. The performance indicator in digital cameras is the number of pixels which relates to the number of photodiodes. CMOS image sensors have a pair of amplifiers per photodiode. In CMOS image sensors, each photodiode is paired with an amplifier. The charge from each element is amplified before it is transferred to the image processing section, which makes it less susceptible to noise during the transfer process.
Image sensor
The process of capturing images with a digital camera involves converting the light of the subject entering through the lens into digital image data before outputting it. The data is converted in the part known as the image sensor. There are two types of image sensors, CCD (Charge Coupled Devices) and CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor). The elements that make up a CCD image sensor can be broadly classified into a light collecting lens, a color filter, a photodiode (light receiving element), and a transfer circuit. The performance indicator in digital cameras is the number of pixels which relates to the number of photodiodes. CMOS image sensors have a pair of amplifiers per photodiode. In CMOS image sensors, each photodiode is paired with an amplifier. The charge from each element is amplified before it is transferred to the image processing section, which makes it less susceptible to noise during the transfer process.
PC sheets, PC resin, PC resin substrate
This is a board-shaped substrate made of polycarbonate resin used for applications that require transparency and impact resistance.
PET film, PET resin, PET resin substrate
This is a film made from polyethylene terephthalate resin that is used for applications requiring strength and durability.
Processing method
What methods of application can be used to treat the substrate?
The antifogging coating film can be treated by spin, dipping, or spray coating. Please inquire for details.
Is it necessary to dry it after application?
After treating the antifogging coating, air-dry it for 10 min and then heat-treat it at a temperature of 100°C or higher. Please contact us for details.
How should we clean the substrate?
If you are cleaning a glass substrate, use alkaline cleaning, etc. to clean the substrate surface by alkaline cleaning in a way that the contact angle of the substrate surface with pure water is less than 10 degrees. Dust on the substrate may lead to defects in the film.
Liquid
What are the conditions for storing the antifogging liquid?
Store the liquid before use in a refrigerator at 10℃.
What type of container should I use to prepare the liquid?
You can use a glass beaker or PE/PET bottle.
How should we deal with any liquid that is attached?
If liquid gets into your eyes, rinse our your eyes with a large quantity of water and seek immediate medical attention. Refer to SDS for product and safety information.
How should we clean the container to which liquid is attached?
Wash and wipe with alcohol before the liquid dries and solidifies to completely remove the liquid.
How should we dispose of the liquid?
Check SDS.
Antifogging coating
How can we confirm the simple antifogging features?
Blow exhaled air on the sample and check that it does not fog up.
Does the film become white if it gets wet?
It is possible that the heat treatment during the antifogging process was insufficient. Adjust the heating temperature and time. Please contact us for details.
Rubbing the film will scratch it.
Antifogging coating has a certain degree of scratch resistance; however, it does not have the function of a hard coat, so if you rub it hard, then scratches may occur.
Can I remove Antifogging coating when reusing defective products?
You cannot remove the antifogging film. Please treat them with a new substrate.
Others
When performing the antifogging treatment, what type of environment should I use?
It is recommended that you perform application work at a temperature of 25°C, humidity of 50%RH, with a cleanliness of Class 1000 or lower.
How can I obtain the antifogging coating sample?
Please contact us.
Contact usCan I apply the antifogging coating to a specified substrate?
Please contact us.
Contact usDo you have any samples?
Please contact us.
Contact usWhat is the price of the antifogging coating?
Please contact us.
Contact us













